As smart homes evolve, so do the devices that keep them clean. Robot vacuums and mops have come a long way, from simple auto-cleaning bots to intelligent assistants that map the home, avoid obstacles, and respond to voice commands. However, there is a common frustration of getting these devices to work smoothly with all the other smart gadgets.
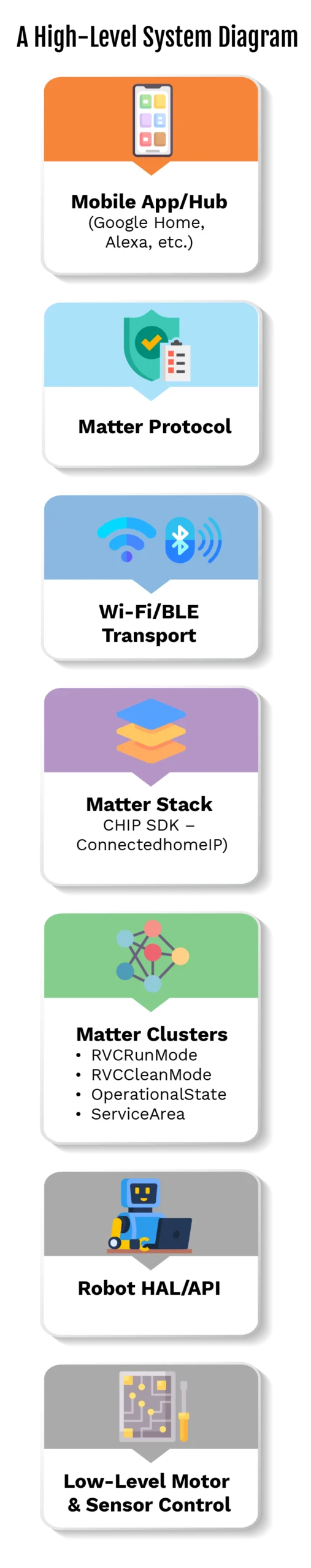
Enter the Matter protocol, a smart home protocol that allows devices from different companies to work together without issues. It sets a shared standard so smart lights, door locks, thermostats, home robots, and sensors can talk to each other. No matter the brand, Matter protocol devices can connect using Wi-Fi, Thread, or Ethernet. This removes the usual confusion when adding new gadgets. eInfochips offers end-to-end IoT solutions, from sensor integration to cloud deployment and analytics—to help bring these innovations to market efficiently.
Matter Matters for Cleaning Robots!
Here is how Matter is making cleaning robots smarter and more user-friendly:
1. Cross-Platform Compatibility
It is possible that one has a robot vacuum that only works with Alexa, but not with Apple Home. Matter compatibility allows the same robot to work across several smart home platforms, like Apple HomeKit, Google Home, Amazon Alexa, and Samsung SmartThings, without requiring a separate app or hub.
2. Faster Setup
Matter uses technologies like Thread and Wi-Fi to make device pairing and control almost instant. Users will spend less time wrestling with apps and more time letting the robot do its job.
3. Local Control = Better Privacy & Speed
Matter enables local control, which means commands like “start cleaning the kitchen” can be sent directly to the robot without routing through the cloud. This boosts response time, reduces internet dependency, and improves privacy.
4. Unified Control
Want to say, “Clean when I leave home,” or “Start cleaning when the baby finishes her nap”? Matter allows integration with one’s entire home routine—lights, thermostats, security systems, and more, hence making cleaning a truly intelligent home experience.
Matter 1.4 Supports the Following:
- Multi-mode cleaning: Vacuum, mop, sweep, polish, and hybrid modes
- Advanced command support: Start, stop, pause, resume, return to dock, locate, and reset
- Zone and area cleaning: Fully supported via the ServiceArea cluster
- Customizable run and clean modes: Use RVCRunMode and RVCCleanMode clusters for user-selectable modes like Eco, Turbo, Quiet, etc.
Operational feedback:
- Real-time status using OperationalState
- Error codes and transitions
- Estimated time to complete
Core Software Architecture (CHIP SDK)
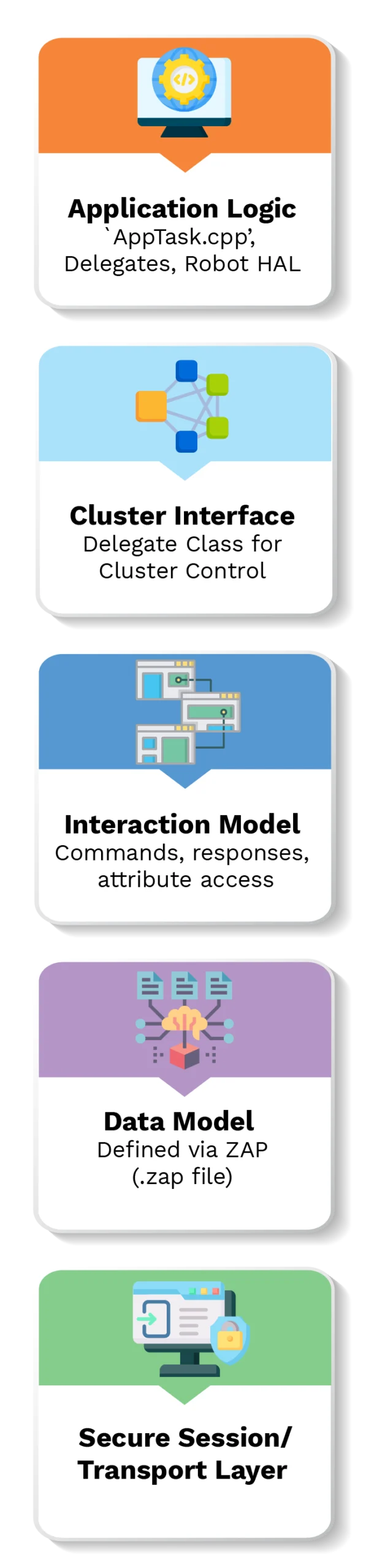
Matter Architecture in a Robot
Define Vendor ID (VID) and Product ID (PID)
| ID | Purpose |
| Vendor ID (VID) | Identifies your company (assigned by CSA) Test VID (0xFFF1–0xFFF5) during development |
| Product ID (PID) | Identifies a specific model you create |
Example Values:
#define CHIP_DEVICE_CONFIG_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID 0x1234 // Assigned by CSA #define CHIP_DEVICE_CONFIG_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID 0x5678 // Your defined product
One can set them in:
- CHIPDeviceConfig.h
- Or dynamically via DeviceInstanceInfoProvider
class MyDeviceInfoProvider : public DeviceInstanceInfoProvider {
uint16_t GetVendorId() override { return 0x1234; }
uint16_t GetProductId() override { return 0x5678; }
};
Defining Device Type, VID, and PID
- Set Device Type ID
For a robot vacuum cleaner (RVC), set the CSA-defined Device Type ID:#define DEVICE_TYPE_RVC 0x0075 // RVC device type ID
In your ZAP file:
<endpoint id="1" deviceType="0x0075"> <server cluster="RVCRunMode" /> <server cluster="RVCCleanMode" /> <server cluster="OperationalState" /> <server cluster="ServiceArea" /> </endpoint>
Robotic Clusters Overview
| Cluster | Purpose |
| RVCRunMode | Set robot mode (Idle, Cleaning, Mapping) |
| RVCCleanMode | Cleaning intensity (Eco, Turbo, etc.) |
| OperationalState | Tracks current state (Idle, Running, Error) |
| ServiceArea | Defines and names zones/rooms |
Cluster Delegate Implementation Example
- Rvc-Mode-Delegates.cpp
void RvcRunModeDelegate::HandleChangeToMode(uint8_t NewMode, ModeBase::Commands::ChangeToModeResponse::Type & response) { RvcDevice::HandleRvcRunChangeToMode(NewMode, response); } - Rvc-Device.cpp
void RvcDevice::HandleRvcRunChangeToMode(uint8_t newMode, ModeBase::Commands::ChangeToModeResponse::Type & response) { switch (newMode) { case RvcRunMode:: ModeIdle: // Stop cleaning and make the robot ideal break; case RvcRunMode:: ModeCleaning: // Robot Start Cleaning break; case RvcRunMode:: ModeMapping: // Robot Map Creation Starts break; default: // Invalid Mode } }
Testing Commands with chip-tool
- Set run mode to cleaning
chip-tool rvcrunmode change-to-mode 1 1234 1 - Read the current operational state
chip-tool operationalstate read current-state 1234 1
ShapeExample: RVCRunMode Workflow
The RVCRunMode cluster in Matter 1.4 allows users to select how the robot should operate — such as Ideal, Cleaning, or Mapping modes. Given below is an example of how a cleaning robot responds to this cluster in the CHIP SDK.
Objective
To allow the user to run modes like cleaning via the Matter app or the Chip-Tool, which then instructs the robot to start the cleaning job.
Workflow Overview
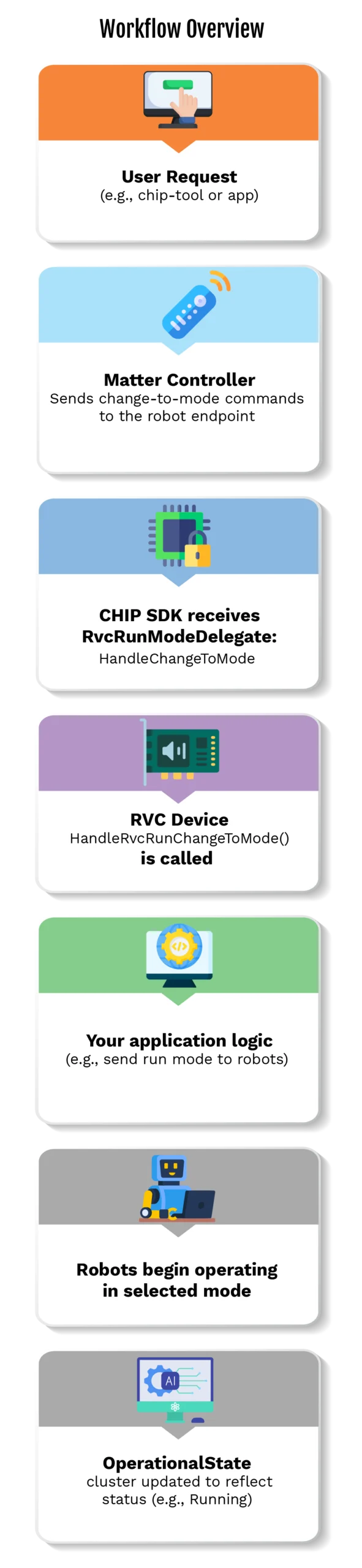
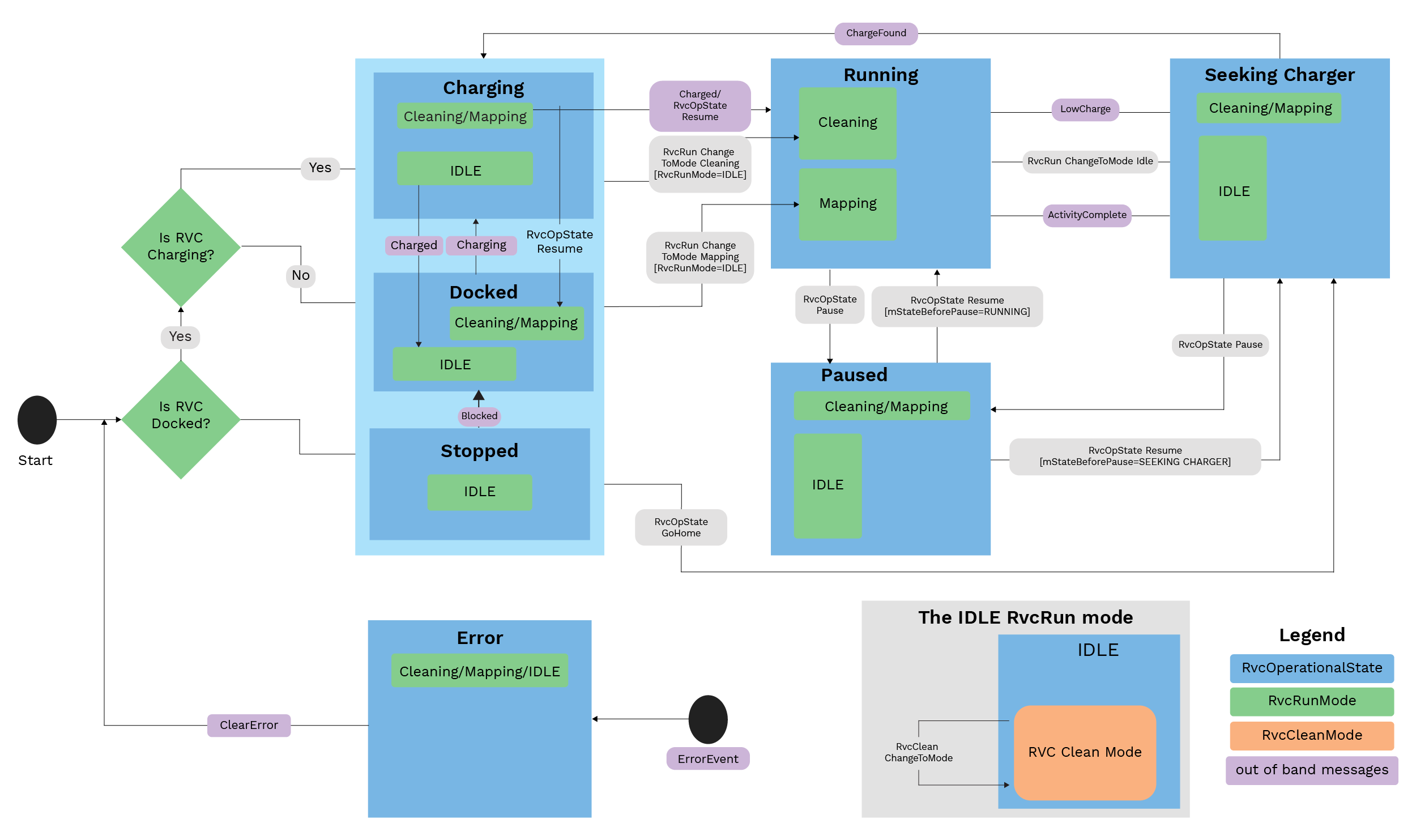
A Cleaning Robot Application State Diagram
Certification Process Before Launch
To launch your product commercially with the Matter logo, follow these steps:
- Join CSA
- Visit https://csa-iot.org and become a member.
- Obtain a Vendor ID
- CSA assigns a unique 16-bit VID for your company.
- Assign Unique Product ID
- Internally define a unique PID for each model variant.
- Setup DAC/PAI Certificates
- Use CSA’s PKI or a trusted CA to obtain:
- DAC (Device Attestation Certificate)
- PAI (Product Attestation Intermediate)
- CD (Certification Declaration)
- Use CSA’s PKI or a trusted CA to obtain:
- Pass Certification Testing
- Matter Test Harness (MTH) or CSA’s Authorized Test Lab (ATL) is used to verify:
- Interoperability
- Attribute compliance
- Commissioning success
- OTA readiness
- Matter Test Harness (MTH) or CSA’s Authorized Test Lab (ATL) is used to verify:
- Submit to CSA
- Submit test results, product metadata, firmware version, and DAC chain to CSA for approval.
Bonus: OTA, Security, and Maintenance
- Secure Commissioning: BLE, QR Code, or NFC-based
- OTA Update: Matter includes OTA requester and provider support
- Security: Every session is encrypted using CASE and attestation
Final Thoughts
By integrating Matter using the CHIP SDK, one gains access to a secure, interoperable smart home ecosystem for robotic products. With standardized clusters, a strong certification path, and growing industry adoption, Matter ensures that one’s robot is ready for the future.