The healthcare delivery teams are adopting new ways of offering accessible and affordable care due to the recent challenges of care team shortage and the increased number of critically ill patients.
The digital health platforms offer tremendous benefits for recording, storing, and processing various patient data and seamlessly integrating it with multiple stakeholder systems across the value chain – including hospitals, insurance providers, and financial institutions.
Agenda
- The digital health platform and applications
- The ecosystem
- Practical challenges and key considerations
- Cloud partner
- Complexity in team development
- QMS and documentation
- External systems integrations
- Data privacy and security
- Maintaining and scaling
- Conclusion
The digital health platform and applications
According to Fortune Business Insights, the market size of digital health is projected to be USD 1,965.30 billion by 2030. Gartner says that by 2024, the healthcare providers who have adopted the digital health platform approach are likely to beat their competition by 80% in the speed of digital transformation and new feature implementation.
The digital health platforms achieve various goals and make day-to-day operations easier for healthcare providers. They capture accurate information from connected devices, reduce the manual intervention of adding data to the portal, provide advanced data analytics, and help in quick decision-making.
These platforms are capable of monitoring health conditions, hosting video consultations, tracking medications, managing doctor’s visits, managing payments, and accessing patients’ health records. Another application is real-time tracking and management of life-saving medical equipment to track various diagnostic, monitoring, and therapeutic devices in hospitals. IoT platform hosted on the cloud integrates these medical assets using cellular or GPS technologies. In case of emergencies, it is very convenient for the nursing staff to track and locate the equipment.
Digital health provides holistic care with the integration of devices to the cloud, patient health data processing, assistance in clinical decision-making and condition management for critically ill patients, and integration with other business systems such as EHR/EMR, insurance, and financial institutions.
The ecosystem
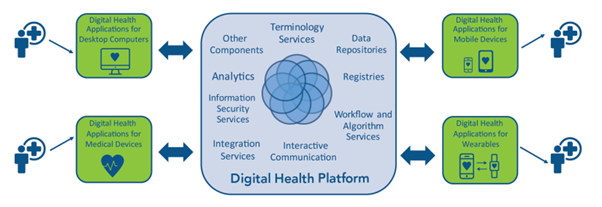
The above ecosystem figure shows the internal components of the digital health platform and its integration with different external applications and devices. The internal components comprise software and information resources, information security services, data repositories, registries, workflows, algorithms, analytics services, and others according to business applications.
The integration with external components includes various software, patient information systems like EHRs, supply chain systems, insurance systems, and patient-centric applications.
Different components in the infrastructure use different messaging standards and protocols. The interoperability among them creates a seamless and unified platform.
Practical challenges and key considerations
Now, let us look at the main challenges that MedTech innovators face while developing, deploying, and integrating digital health platforms.
1. Cloud partner
It is important to choose the right cloud partner for digital health applications. Each cloud platform provider has differences in architecture, infrastructure components, services, offerings, and pricing models. Sometimes, it is difficult to troubleshoot on the cloud platform, and it also causes security and compliance gaps. The prime factors while selecting the right cloud platform are compliance, security, SLA, pricing, reliability, manageability, migration strategy, support, and services.
2. Complexity in Team Development
A strong team plays a vital role in successfully developing a digital health platform timely. This team consists of software developers, cloud architects, software testers, security experts, compliance and privacy experts, DevOps engineers, and analytics engineers. The resources need an in-depth understanding of the selected cloud platform along with domain expertise. It is cumbersome for the organization to find niche talent; even harder is to retain them after project completion.
3. QMS and documentation
Evolving compliance and regulatory standards require an experienced team to set up a robust quality management system. An unregulated digital health platform delays the time to market and makes the global product launch complex. Additionally, creating and maintaining large documentation of design history files, risk management files as per ISO 13485, IEC 62304, and FDA SaMD-compliant is a lengthy process for the MedTech innovators.
4. External and partner system integration
The digital transformation in healthcare is replacing proprietary solutions to open source and interoperable solutions. The digital health platform should be seamlessly integrated with multiple leading Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, insurance provider systems, payment institutions, and supply chain systems.
The key challenge here is to convert data into a single format and compile it after capturing data from various sources (wearables, medical devices). Also, data integration needs to follow HIPAA compliance with diverse data files, sizes, and formats. HL7 is the interface used for processing the data in an interpretable format, and the solution should be compatible with HL7 standards.
5. Data privacy and security
Digital health platforms capture and process sensitive personal health data of users, so the solution needs to protect their privacy. Also, there is a big concern about data sharing in integration with external systems as it can breach security and allow access to patients’ critical information from unwanted sources. Data governance provides permits to access specific data for a particular duration. The solution should use HIPAA and GDPR-compliant cloud providers to minimize the security risk.
6. Maintaining and scaling
Many solutions start with a basic application and later grow with new features added to it. When it achieves scale, challenges also increase for maintaining the entire environment. Some of them are, managing the large cloud infrastructure, optimizing the increased cloud cost, and ensuring end-to-end security, reliability, and uptime. The penetration in wider geographies and global markets also requires localization support – multi-language, local regulations, and cultural norms.
Conclusion
Digital transformation is becoming more patient-centric; and with the huge amount of patient data available, the analysis has become crucial for diagnostics, monitoring, and therapeutics to deliver value-based care services. If implemented correctly, the digital health platform can assist in shifting the care delivery model from a traditional approach to a personalized approach.
We at eInfochips, engage with global medical and life sciences clients to design, develop, deploy, and maintain digital platforms for a variety of applications, remote patient monitoring, home diagnostics, wearables, consumer health devices, and many more. We have strategic and deep-rooted partnerships with leading cloud providers (AWS and Azure) and have access to their next-gen AI labs.
Want to know more about our digital healthcare solution? Contact our experts now!












