We are surrounded by wirelessly connected electronic and mechanical devices such as cars and consumer electronics, and they have become an integral part of our daily lives. Many such devices are connected to the internet or to host devices via Wi-Fi, cellular data, or Bluetooth. It is particularly important to upgrade their system firmware and applications to ensure they work properly without any glitches.
Why OTA (Over the Air) Firmware Upgrades for Automotives are Important
- Improved performance: Firmware updates can address bugs and improve the overall performance of the cars; especially in EVs firmware updates can enhance the performance of the battery management system while increasing the battery life and making the process of charging & discharging more proficient.
- Enhanced safety: Firmware updates can also include important safety features and improvements that help prevent potential hazards and protect the vehicle and its occupants.
- New features and capabilities: Upgrading the firmware can also add new features and capabilities to the ECUs and the battery management system, such as improved battery monitoring and diagnostics, remote access and control, and improved integration with other systems in the vehicle.
- Cost savings: Upgrading the firmware over the air eliminates the need for physical updates and maintenance, which can save time and money for both the vehicle owner and the manufacturer.
- Improving Product Development Cycle Time –With the OTA (Over the Air) firmware updates the waiting period of the car could be decreased by first getting the car ready for the delivery in the field and performing the software upgrades later.
Over the Air Firmware Upgrade for Automotive Concept
Firmware upgrade over the air (FOTA) is a concept in which the firmware of a vehicle can be updated wirelessly, without the need for physical access to the vehicle. The update is typically sent to the vehicle via a cellular or Wi-Fi connection and is then installed by the vehicle’s onboard computer. This allows for the correction of bugs, the addition of new features, and the improvement of the vehicle’s overall performance. FOTA is becoming increasingly popular in the automotive industry, as it allows for more efficient and cost-effective maintenance of vehicles.
It is a straightforward but lengthy process. Its development is hectic for many developers as it includes security prospects in every phase of the process. Lots of encryption techniques need to be implemented to secure the data transfer and intelligent bootloader and monitor the process to sort problems while upgrading firmware.
The few simplified steps of the firmware update process are
- Design the firmware structure and develop the firmware code.
- Develop security algorithms and protocols for data transfer and authentication.
- Develop a secure bootloader for the firmware.
- Develop the firmware update procedure to ensure successful and secure firmware upgrade.
- Test the firmware update process and validate the updated firmware.
- Deploy the firmware upgrade and post-deployment support.
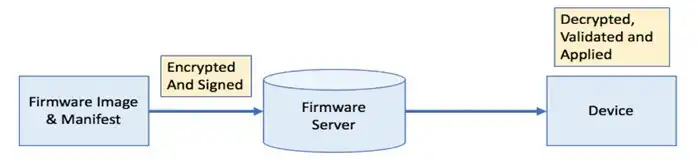
The following diagram shows the process of firmware upgrade over the air.
Firmware package is encrypted, signed, and uploaded to Firmware Server. The End Device or user product requests for firmware upgrade and after authentication it downloads the firmware image and manifest. The firmware package is then unpacked and decrypted locally. The changes in the upgrade will be verified and after the changes are verified, it will be applied with the end user’s consent. The communication between end device and firmware server happens over the air i.e., through Wi-Fi or cellular data. In some cases, there is a master device which pulls firmware image and transfers it to the end device like wearables via Bluetooth.
Risks In the Process of Firmware Upgrade for Automotives
Over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates for automotive systems have become increasingly common as cars have become more connected and reliant on technology. However, these updates also come with certain risks that need to be considered.
Cybersecurity risks in the Communication channel
The firmware image is encrypted and stored on the server. When the end device requests to download image, the server starts transferring data. This transmission is encrypted such that anybody other than the end user’s device will not be able to decrypt and access the data. However, there is always a risk of data being hacked by hackers. Data can be snooped by hackers while it is getting transferred to your automotive via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth or cellular data.
Intra-system data transfers such as from a SoC (System on Chip) to external flash, can pose a security threat if a malicious party gets physical access to the end device.
Moreover, OTA updates can introduce vulnerabilities into automotive systems, making them more susceptible to hacking and other cyber-attacks. Hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive data, control the vehicle remotely, or cause it to malfunction.
Data corruption
When the end device downloads an image from server it might get corrupted due to interrupted internet connection. This corrupted image leads to malfunctioning of device if it is flashed. For example, Ashly devices disable themselves when any internet interruption happens. For such scenarios, the end device should also be equipped with a mechanism to detect any corrupted data, such as by verifying the CRC of the data before it is loaded onto the device. If CRC does not match, then the device reinitiates the downloading process. In android, it is important to ensure that the bootloader of the device is not altered or unlocked by the user, as this can lead to complete data loss.
Interference With Other Systems
OTA updates, if not updated properly, can interfere with other systems in the vehicle, causing them to malfunction or stop working altogether. This can lead to safety risks, such as the failure of critical systems like the brakes or steering.
Incompatibility With Existing Systems
OTA updates can be incompatible with existing systems in the vehicle, causing them to malfunction or stop working altogether. This can lead to safety risks, such as the failure of critical systems like the brakes or steering.
Network dependence
Over the Air Firmware updates in automotives require a reliable and stable internet connection, which might not be available in some areas. This can make it difficult to update the firmware on the vehicle, and it could cause the vehicle to be left with outdated and vulnerable firmware.
Privacy
Firmware updates can be used to collect personal data of the user like location, speed, etc. thus leading to privacy concerns.
Inadequate User Awareness
Most important term in this process is user awareness. Manufacturers produce certain rules like keeping battery charge level above 50% or uninterrupted internet connection to download image or end devices should be in range to host devices etc. to upgrade firmware without any failure. If these rules are not followed, there is a fair chance of firmware image corruption which can lead to device failure.
Wrapping Up
To mitigate these risks, automotive manufacturers and suppliers need to implement robust security measures, such as encryption and authentication, to protect their OTA update systems from cyber-attacks. They should also thoroughly test updates before releasing them to ensure that they are compatible with existing systems and will not interfere with the vehicle’s performance or safety.
Day by day digital services are getting advanced. Every day, new changes or upgrades are being introduced and it is a never-ending process. Automotive companies are introducing new features that can be upgraded over the air to ensure that their automotives function efficiently. The risks in the firmware upgrade in automotives can be minimized by giving proper security to every phase of the firmware upgrade process. Modern encryption techniques are vastly secured for channels and data. Advancements in the package error detection lowered down the chances of data corruption of the package. Internet connection and power backup are two recommended factors in uninterrupted upgrade process.
Checkout our einfochips’ services for automotives industry including EVs and embedded systems and software development or contact us with your queries and we will get the best possible answer to your business problems.