The Electric Vehicle (EV) market is expanding, and with it, the demand for intelligent, safe, and compatible charging infrastructure is increasing. The demand for EV vehicles is projected to exceed 12.2 million by 2035, as mentioned in the Electric Vehicle Sales and the Charging Infrastructure Required Through 2035 research paper, which highlights the need for robust and future-ready charging protocols. The core of EV charging communication is “Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP),” a widely adopted, open-source protocol that allows charging stations to communicate efficiently with Charging Station Management Systems (CSMS).
In this blog, we will explore: OCPP 2.0.1
- OCPP ecosystem architecture
- Difference between OCPP 1.6 and 2.0
- Benefits of OCPP 2.0
- Practical migration steps
What is the Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP)?
Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) was developed by the Open Charge Alliance (OCA) and is a standardized protocol that enables Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations to communicate with Charging Station Management Systems (CSMS). OCPP’s earlier versions, such as 1.2 and 1.5, provided basic functionalities like RFID-based authorization and simple transaction handling, laying the foundation for later enhancements. It helps ensure that the charging infrastructure is interoperable, vendor-neutral, and scalable.
Version Highlights
- OCPP 1.6: Released in 2015, the protocol supports both JSON over WebSocket and SOAP. It is widely used and is reliable for basic EV charging needs, introducing basic smart charging capabilities that enabled foundational interoperability and energy management functions.
- OCPP 2.0 / 2.0.1: Released in 2018 and refined in 2020 (2.0.1), it offers a comprehensive set of features including better security, advanced smart charging, and support for future-ready EV technologies.
The OCPP Ecosystem: Visual Overview
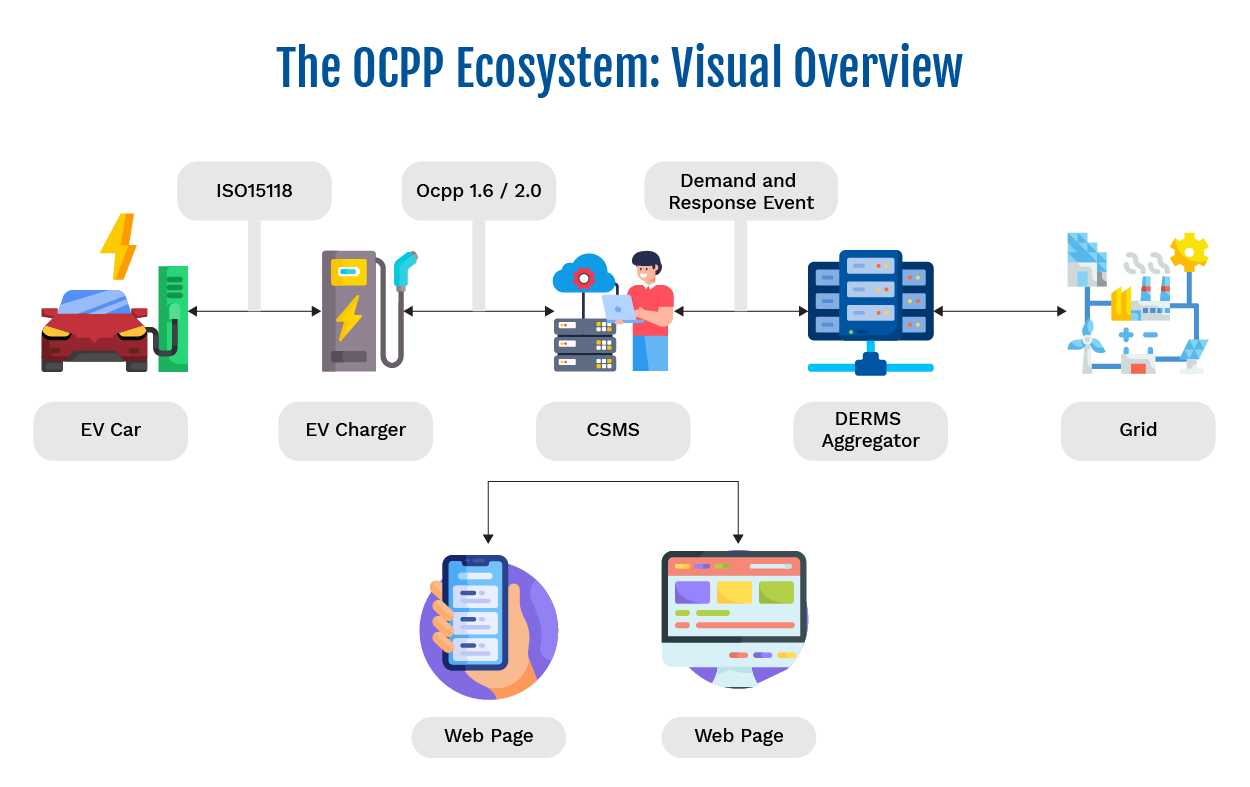
The OCPP ecosystem ensures seamless communication between the charger and CSMS, shaping the evolving EV charging landscape. OCPP introduced support for new features and enhancements in each version, expanding the range of use cases and improving transaction handling and data efficiency. Various standards and interfaces are supported by OCPP, promoting interoperability across the network. The Charging Station Management System acts as a central management system for the network, coordinating device management, transaction handling, and smart charging functionalities. By standardizing communication, OCPP helps overcome the limitations of proprietary systems and fosters universal compatibility.
All its components are mentioned below:
- Electric Vehicle: Communicates with the EV charger. For plug-and-charge communication, it uses the ISO 15118 Protocol.
- Charger: The charger (also referred to as electric vehicle supply equipment, or EVSE) connects to the server and facilitates data transmission using the standardized OCPP 1.6 or 2.0.1 protocol over a WebSocket connection. This protocol helps to communicate with the charger and CSMS seamlessly.
- Charging Station Management System: Communicates with the charger, monitors energy usage, and manages remote commands. It transfers data to the mobile and web applications from the EV charger for the user Interface. It serves as the central management system for the charging network.
- Charge Point Operator: The charge point operator (CPO) is responsible for managing and operating EV charging stations, handling diagnostics, firmware updates, and enabling features like roaming and smart charging through communication protocols such as OCPP.
- DERMS Aggregator: Distributed Energy Resource Management System (DERMS) aggregators receive Demand Response (DR) event details from the energy provider. These events are forwarded to the CSMS server that processes and translates them into smart charging commands, which are then sent to the charger.
- Grid: It is the energy provider; to maintain a stable load on the grid, Energy providers send event information to DERMS aggregators.
Comparison: OCPP 1.6 vs OCPP 2.0.1
Here is a summary of the key differences between OCPP 1.6 and OCPP 2.0.1, highlighting the latest advancements, new features, and supported standards to help you make informed decisions.
| Feature | OCPP 1.6 | OCPP 2.0.1 |
| Profiles |
|
|
| Security | Simple encryption and basic authentication, which includes TLS-encrypted communication. | Strong security features, including certificate-based mutual TLS encryption, secure boot, encrypted logs, and advanced security settings using X.509 certificates, are available to enhance system protection. |
| Smart Charging | Limited capabilities for efficient load balancing and task scheduling. It has predefined charging profiles such as TxProfile, TxDefaultProfile, and ChargingStationMaxProfile. | Advanced features such as dynamic load management, flexible charging profiles, and adjusting load based on demand, which allow real-time updates of charging profiles based on factors such as grid conditions, energy prices, or vehicle schedules. |
| ISO 15118 Integration | Basic support for ISO 15118 via extension on 1.6. | Fully supports plug-and-charge via ISO15118, which enhances security and better device management, and supports Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), allowing for smooth interaction between electric vehicles and the grid. |
| Diagnostics and Monitoring | Basic diagnostics log upload and the ability to report the charger status. | Advanced Diagnostics with charger security log request and has Advanced monitoring commands like SetMonitoring and GetMonitoring for real-time monitoring. |
| Firmware Updates | Manual and limited remote update capabilities. | Secure firmware management with verification of authenticity and integrity of updates. |
| Transaction Management | Tracks start and stop events of charging sessions. | Improved session lifecycle control with cancel, suspend, and resume functions; better tracking for billing accuracy. |
Making informed decisions about which OCPP version to implement is crucial. Understanding these key differences and the latest advancements will help you make informed decisions when upgrading or deploying your EV charging infrastructure.
Why OCPP 2.0.1 Matters for Smart Charging Capabilities
OCPP 2.0.1 is not just a version upgrade—it is a strategic move toward smarter EV infrastructure. Here is why:
1. Future-Proofing EV Infrastructure
It is built to support plug-and-charge and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), making it compatible with the latest EV technologies. OCPP 2.0.1 incorporates the latest advancements in EV charging technology, ensuring your infrastructure remains up to date.
2. Stronger Cybersecurity
It fully supports certificate-based authentication with TLS encryption, secure firmware updates, and encrypted diagnostics logs, delivering enhanced security to address evolving cybersecurity threats.
3. Advanced Smart Charging
The OpenADR features like Dynamic Load Management, real-time price signals, charging profiles based on priority, and grid availability make OCPP 2.0.1 ideal for modern energy ecosystems.
4. Rich UI Experience
We can show helpful messages on EV charger screen and play audible alerts on them. This feature is designed to improve the overall experience for drivers, making interactions smoother and more intuitive while they are charging their vehicles.
5. Remote Management and Maintenance
OCPP 2.0.1 introduces the Modular Device Model that enables full visibility and control over each hardware component. These capabilities help reduce operational costs by streamlining maintenance and minimizing the need for on-site interventions.
6. Real-Time Monitoring
OCPP 2.0.1 helps CSMS to communicate with charge points for real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and maintenance. It includes “set monitoring” and “get monitoring” features for tracking operational health.
Migration from OCPP 1.6 to 2.0.1: Strategy and Steps
OCPP 2.0.1 is not backward compatible with OCPP 1.6, so careful planning is essential.
1. Check Hardware Readiness
- Ensure your electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) supports OCPP 2.0.1 firmware and has sufficient memory and processing power. OCPP 2.0.1 must be supported by both the hardware and firmware.
2. Upgrade Charger Firmware
- Coordinate with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) or firmware teams to implement:
- OCPP 2.0.1 commands and messages. OCPP 2.0.1 introduced support for new commands and features.
- Secure communication features (TLS, signed firmware).
- Prepare a firmware update package to migrate from OCPP 1.6 to OCPP 2.0.1, while preserving all existing configuration settings.
3. Update CSMS
- The CSMS must support both OCPP 1.6 and OCPP 2.0.1 protocols, and the firmware should be capable of switching between OCPP versions based on configuration.
4. Parallel Operations
- Operate OCPP 1.6 and 2.0.1 chargers in parallel and build CSMS components that support both versions.
5. Test and Certify
- To verify the functionality of version 2.0.1, please ensure that all your functional tests confirm it is working as expected with versions 1.6 and 2.0.1. Additionally, conduct your load testing to check if the system can handle the same load on both the charger and CSMS sides with versions 1.6 and 2.0.1. For OCPP compliance, use the Open Charge Alliance (OCA) certification tools to test the end-to-end flows and ensure everything is compliant. The OCA offers the OCTT tool that includes over 400 test cases for validating version 2.0.1 protocols. For OCPP 2.0.1, depending on your implementation and certification needs, OCA provides two types of certificates: the Core Profile Certification and the Core Profile and Advanced Profiles Certification. A comprehensive set of features and test cases must be validated. Make sure to plan your certification accordingly.
6. Security Onboarding
- Deploy:
- Certificate-based authentication.
- Secure firmware upgrade workflows.
- Use transport layer security (TLS) for secure communication.
- Training for teams handling key and certificate rotation.
Final Thoughts
OCPP 2.0.1 represents a foundational shift—empowering EV charging networks to become smarter, more secure, and scalable for future energy demands. While OCPP 1.6 has served the industry well, transitioning to 2.0.1 unlocks vast potential for smart grid integration, richer diagnostics, and seamless EV user experience.
As the EV industry continues to grow, adopting OCPP 2.0.1 is not just a technical upgrade—it is a step toward building a sustainable and future-ready energy ecosystem.
Ready to upgrade your EV infrastructure to OCPP 2.0.1? Contact us today to learn more about implementation strategies and best practices.











