Testing of mobile apps is quite cumbersome and challenging as it requires testing apps on multiple variants, operating systems, and devices. Also, in most cases, it is difficult to achieve complete test coverage for all the features with manual testing. Additionally, mobile apps undergo frequent releases compared to other kinds of applications such as web or desktop, which require faster turnaround time, from testing to final release. To deal with these challenges, software enterprises have started emphasizing on automating mobile application testing.
There are various test automation frameworks and tools available for mobile test automation. These frameworks can be used for testing both Android and iOS apps as well as native, web and hybrid apps. Mobile app automation can be a massive undertaking, which can complicate the process if a wrong or irrelevant tool is selected. Hence, you need to choose the right tool/framework to get the desired results for your testing effort. Selendroid is one of the popular mobile test automation frameworks for automating mobile testing.
Let’s learn about Selendroid in detail.
1. What is Selendroid?
Selendroid, as the name suggests, is a Selenium-based test automation tool for testing various types of mobile applications – Android native, hybrid and mobile web applications. The best feature of Selendroid is its Opensource architecture.Selendroid can be also used for testing on emulators and real devices. It also can be integrated into the Selenium Grid for scaling and parallel testing on multiple nodes.
Selendroid is a #mobiletestautomation framework for automating testing of #Android Native, Hybrid & Mobile Web applications via @einfochipsltd
2. Features of Selendroid
- Requires no modification of Application Under Test (AUT) to automate
- Provides easy interaction with multiple devices or simulators
- Supports hot plugging of hardware devices
- Supports gestures
- Supports multiple Android APIs
- Follows the same concept for automating native or hybrid applications
- Provides built-in Inspector to develop and simplify the test case
- Starts existing emulators automatically
- Allows extending at runtime with your own extensions
- Helps find UI elements by different locator types
3. Selendroid Architecture
Selendroid is based on the Android Instrumentation framework. The Selendroid tests are written using Selenium Webdriver client API, which is also called as Selenium 2 client. Hence, it supports full integration with existing Selenium frameworks. It is also compatible with JSON Wire Protocol.
The following figure describes the architecture of Selendroid.
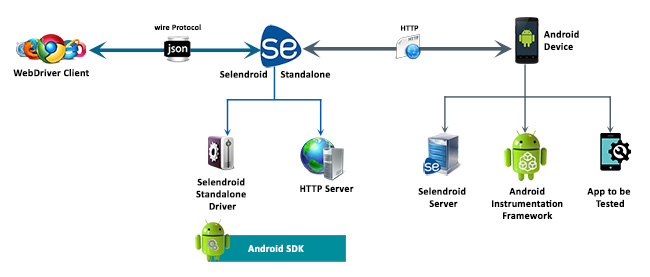
Selendroid contains 4 major components:
- Web Driver Client
- Selendroid Server
- Android driver app
- Selendroid Standalone
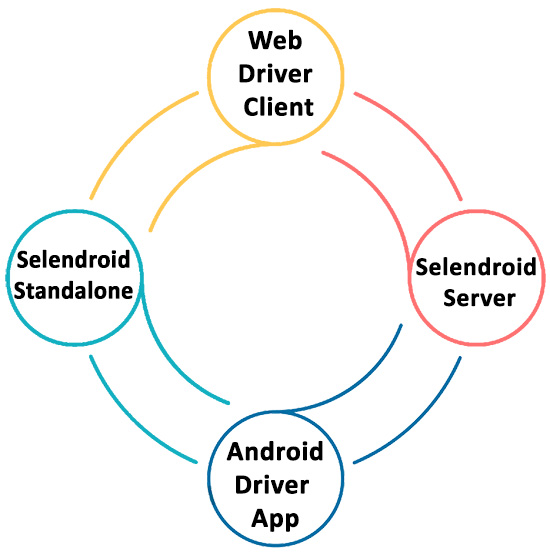
- Web Driver Client: It is a Java client library based on Selenium, which should be installed on the computer. It is used to develop the test cases.
- Selendroid Server: This server runs on the device and is implementing the JSON Wire Protocol for the app under test on Android device or simulator. This is the main component of Selendroid architecture responsible for app automation.
- The central driver class is DefaultSelendroidDriver for both native app and webview. The web view related driver class is SelendroidWebDriver and native class is SelendroidNativeDriver.
- Android Driver App: It is a built-in Android driver web view app to test the mobile web.
- Selendroid Standalone: The central driver class is SelendroidStandaloneDriver that acts as a proxy between the Selendroid-client and the Selendroid-server. It starts an Android emulator, creates) a customized Selendroid-server for the application under test (AUT and installs everything on the device. After the session is initialized, subsequent requests are directly forwarded to the server on the device and the response is routed back to the client.
4. Steps to set up a Selendroid environment for Test Automation
Steps to set up a Selendroid environment for Android Apps Test Automation:
- Install the Java SDK
- Download Android SDK and set up Android path on your machine
- Download Selenium jar files and test applications from Selendroid
- Set-up and launch the Selendroid tool into your PC
- Setup the Android Emulator or attach the real/physical device with USB
Steps to set up a Selendroid environment for Mobile Web Test Automation:
- Download the Selendroid Standalone Java libraries
- Install Android SDK from the Android development site
- Set up an Android development environment and create an Android Virtual Device by using Android Virtual Device Manager
- Start the Android virtual device
- Create a Java Project, add Selendroid Standalone libraries and JUnit libraries in the build path
- Add a JUnit test class to the project
- Run the JUnit test
- Check the test Result
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
eInfochips provides a unified Test Automation Framework that enables simultaneous testing across the web and mobile platforms, ensuring high-quality solutions and 40% reduction of effort over traditional automation methods. It also provides early automation, reducing the operating costs and enabling faster time-to-market.
To know more, read our white paper on Unified Test Automation solutions.











