Introduction
A Content Delivery Network aka CDN is a network of data servers distributed globally to ensure that the content reaches its users instantly. It is able to do that by consciously placing the data centres also known as points of presence (POPs) closer to the geographical location of its audience/users i.e., by hosting content nearer to the places that have high number of users. For example, for the end users situated in Europe, the content is hosted in Europe to decrease the loading time as compared to the content hosted in the USA (United States).
The content majorly is static in nature like HTML/CSS/JS files, images, videos, text files, etc. Moreover, the delivery of dynamic content such as video and audio streaming can also be done using CDN.
The CDN is a go-to solution for fixing site issues impacting page load speed. Since CDN is on a separate server, the original application server can serve more users without worrying about overloading.
How a CDN works and caches content?
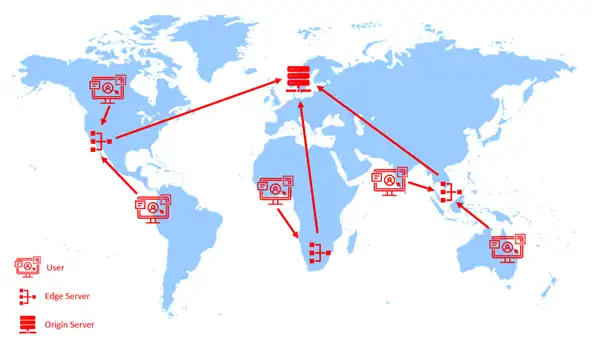
Content Delivery Network relies on servers like source server and edge server. The source server or sometimes called the origin server is the server which hosts the full version of an application or files while the edge server, a group of servers that caches and deliver the web content, stores the copy of content hosted on the origin server.
The edge servers are spread around the world, which helps in reducing the latency while accessing the web content. These servers also provide security to the origin server along with caching the content. Since the user accesses the edge server, not the source server, origin server has reduced traffic.
When a user tries to access the content, based on the source IP address, the approximate location is determined. Based on that location, the closest edge server serves the request of that user. Initially, the edge server doesn’t have all the content, so it requests the origin server and caches the content which is then forwarded to the end users. This is how caching works. The effectivity of CDN depends on the placement of edge servers. They should be placed as per the traffic of end users.
Let’s understand, what will be the user experience with and without CDN through 2 examples.
Without CDN
A business named XYZ’s website is hosted on a server situated in the United States (USA) and a user from India tries to access it. Since, these two countries are on two separate continents with an ocean and another continent in between them, it may take up to five seconds for the content to reach, which is quite a long time considering modern content delivery standards.
With CDN
Now, if XYZ uses CDN and strategically deploys data centres or edge servers in another Asian country like Singapore or Japan, or for that matter, even in India. The initial part of content can reach within two seconds, which is a 50% reduction in time, with the help of the edge server placed nearby, and then the edge server can relay the remaining content from origin server to the user. It enhances user experience and decreases bounce rate which is exceptionally good for the business revenue.
Salient benefits of using CDN
- Reduced load time of an application – Quick caching of files and edge server being closer to an end user results in drastic improvement of the load time of webpages and static files. It helps in improving the Search Engine Optimization (SEO) of a website to achieve better ranking on search engines.
- Cost-saving from the bandwidth usage – The host server is not fully occupied in loading the content which eventually helps in saving the cost of the bandwidth. The CDN server delivers the requested content quickly as per the location of a user and built-in optimization techniques like caching.
- Improved security – The CDN servers protect the origin server from various network-based threats like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. The protection is due to less data transfer from the single origin server. The edge servers provide a cover making the origin server virtually invisible.
- Quicker content distribution – Many aspects of web applications like e-commerce stores, entertainment sites and multimedia-based advertising apps are heavily dependent on redundancy and availability of content. The CDN helps in achieving such distribution without worrying about traffic or hardware/network failures.
Conclusion
The immersive user experience and superior quality performance are the backbone for any successful application in the digital world aiming to conquer the top spot in their respective industry. CDN is a great tool to achieve seamless content delivery for your cloud application.
There are many cloud-computing and SaaS (Software as a Service) companies that provide CDN solutions and those can be integrated seamlessly.
eInfochips has in-depth experience in developing geographically distributed and multi-tenant cloud applications using innovative technologies. If you are exploring a partner having expertise in IoT, Wireless, Security, Sensor-to-Cloud solutions, etc then contact us.