In today’s ever-changing cybersecurity threat landscape, one important factor that becomes key to protecting sensitive information is cryptography. It Derived from the Greek words “kryptos” meaning hidden and “grapho” meaning write, cryptography serves as both an art and a science, seamlessly transitioning from ancient practices into the digital age. In this blog, we examine the importance of cryptography in network security, exploring its technology and methods that enable it to solve modern network problems.
One of the main functions of cryptography is encryption, which uses cryptographic algorithms and keys to convert plaintext into ciphertext. This technique ensures that the message is unreadable to anyone who does not have the relevant decryption key, thus preventing unauthorized access and eavesdropping attempts. Whether it is protecting financial transactions, protecting personal communications, or protecting sensitive government data, encryption is essential to maintain privacy and confidentiality in the ongoing world.
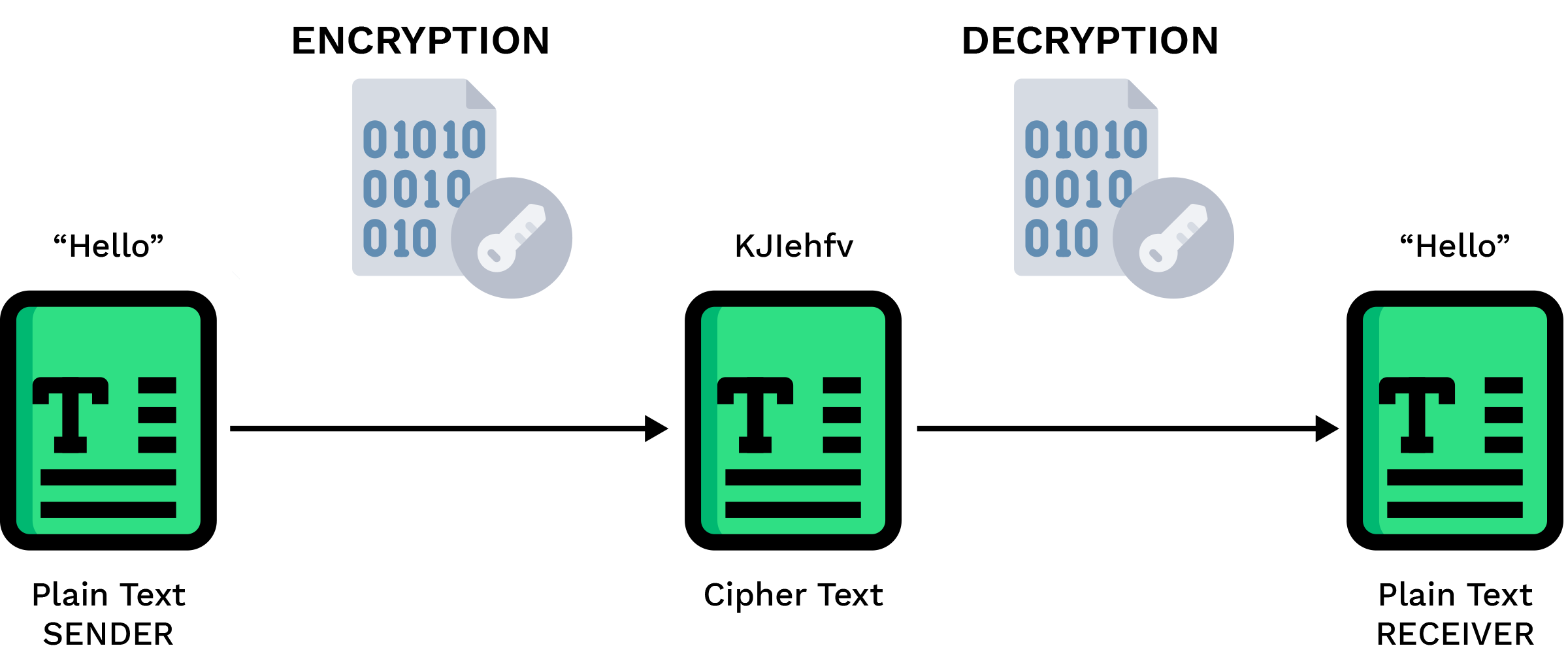
a sender wishes to transmit a message “Hello” to the receiver securely. Through the process of encryption, the message is transformed into an unreadable form using an encryption key before being sent. Upon reaching the receiver, the encrypted message is decrypted using the appropriate decryption key, restoring it to its original plaintext form. This simple example underscores the fundamental concept of cryptography, where sensitive information is encoded for secure transmission and decoded upon receipt, ensuring confidentiality and integrity throughout the communication process.
Cryptography plays an important role in maintaining data integrity, ensuring that data is not tampered with and protected from tampering while being transmitted or stored. By creating cryptographic hashes or digital signatures, organizations can verify the authenticity and integrity of data and detect unauthorized changes or error attempts. This capability is important in critical areas such as healthcare, where the integrity of patient information and medical records must be maintained to protect patient safety and privacy.
Cryptography serves as the foundation of security by ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of information. Encryption makes information unreadable by unauthorized persons by using algorithms and keys to convert plaintext into ciphertext. This ensures that information is protected from prying eyes even if it is interrupted.
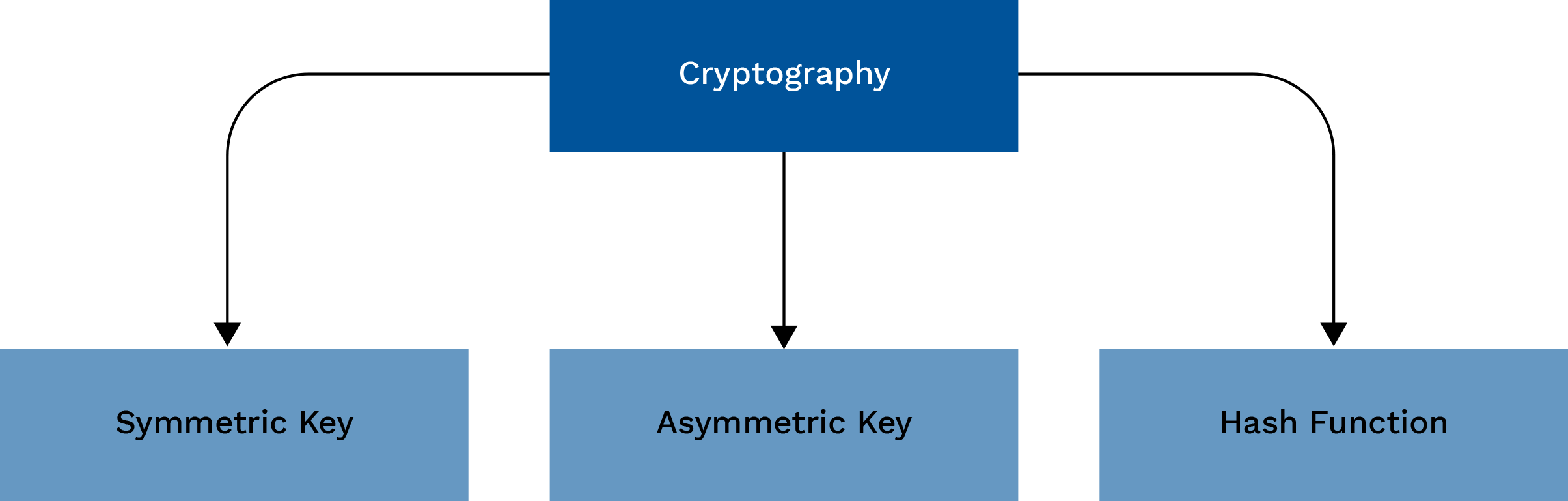
Symmetric encryption:
- In symmetric encryption, the same key is used for encryption and decryption.
- Fast and effective for encrypting large amounts of data.
- Examples: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), DES (Data Encryption Standard) and 3DES (Triple DES).
Asymmetric Cryptography (Public-Key Cryptography):
- Asymmetric cryptography uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key.
- The public key is used for encryption and the private key is used for decryption.
- Widely used for exchanging security keys, digital signatures and encryption in situations where distribution security is difficult.
- Examples: RSA (Rivest -Shamir-Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curve Crypto) and Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
Hash Functions:
- The hash function accepts an input (or message) and produces a constant output called the hash value or hash.
- They are used to verify data integrity, create digital signatures and store passwords securely.
- One-way arithmetic operation makes it impossible to reverse the process and get the original input from the hash value.
- Examples: SHA-256 (part of the SHA-2 family), SHA-3, and MD5 (though MD5 is considered weak for many security applications due to vulnerabilities).
Role of Cryptography in Cybersecurity:
- Confidentiality: Cryptography ensures the confidentiality of sensitive information by encrypting data, making it unreadable without the decryption key. This safeguards personal data, financial transactions, and classified information from unauthorized access.
- Integrity: Data integrity is crucial in cybersecurity. Cryptographic hash functions ensure that data remains unaltered during transmission or storage. Any tampering with the data alters the hash value, alerting the system to potential unauthorized modifications.
- Authentication: Cryptography establishes the authenticity of users, devices, or entities in digital environments. Digital signatures validate the origin and integrity of data, allowing communication partners to trust the identity of the sender.
- Key Management: Security, distribution and management of encryption keys are important. Key management prevents unauthorized access and ensures the overall security of the cryptosystem.
- Secure Communication: In an interconnected world, secure communication is essential. Protocols like SSL/TLS utilize cryptography to create secure channels for transmitting sensitive data over the Internet, ensuring secure online banking, e-commerce transactions, and confidential business communications.
Challenges and Future Trends:
While cryptography is a robust defense against many cyber threats, challenges persist. Quantum computing poses a threat to existing encryption algorithms, driving research towards anti-quantum encryption solutions. Additionally, the growing sophistication of cyber-attacks demands constant innovation in cryptographic techniques.
Looking ahead, post-quantum cryptography gains traction, focusing on algorithms resilient against quantum adversaries. As technology advances, cryptography will evolve to meet new challenges, ensuring the digital world remains secure.
Exploring the Significance of Cryptography:
Cryptography serves as a vital component in securing data, communications, and identities in the digital era. Its significance extends beyond mere encryption; it fosters trust, ensures privacy, and underpins the integrity of digital interactions. Let’s delve deeper into the multifaceted role of cryptography in cybersecurity:
- Privacy Protection:
Cryptography safeguards privacy by encrypting sensitive information, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access it. Whether it’s personal conversations, financial transactions, or medical records, cryptography shields data from unauthorized eyes, preserving individuals’ privacy rights in an increasingly digital world.
- Trust Establishment:
Trust is the cornerstone of any digital transaction. Cryptography helps establish trust by providing mechanisms for authentication and verification. Whether it’s validating the authenticity of a website using SSL/TLS certificates or verifying the integrity of software downloads through digital signatures, cryptography instills confidence in online interactions, fostering trust between users and systems.
- Regulatory Compliance:
With the proliferation of data privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, organizations are under increasing pressure to protect sensitive information and uphold privacy standards. Cryptography plays a pivotal role in regulatory compliance by enabling organizations to encrypt data at rest and in transit, thereby mitigating the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with stringent data protection regulations.
- Defense Against Cyber Threats:
In today’s threat landscape, cyber-attacks are becoming more sophisticated and pervasive. Cryptography serves as a frontline defense against cyber threats by thwarting unauthorized access, data tampering, and eavesdropping. By encrypting data and securing communication channels, cryptography mitigates the risk of ransomware attacks, data breaches, and other cyber threats, thereby enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
- Innovation Enabler:
Cryptography fuels innovation by enabling secure digital interactions and unlocking new possibilities in areas such as blockchain, IoT (Internet of Things), and cloud computing. From securing smart contracts on blockchain networks to encrypting communication between IoT devices, cryptography paves the way for transformative technologies that drive digital progress while ensuring security and privacy.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cryptography plays an important role in cybersecurity by ensuring the protection, integrity, and trust of data in the digital economy. At Einfochips we have our IoT security division, we specialize in providing security suggestions and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Our tailored solutions help businesses fortify their defenses against cyber threats, navigate regulatory requirements, and maintain a secure digital environment and their product.












