What is SIEM?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a group of services and technology describing an organization’s information security.
SIEM includes two technologies with:
- a) Security Information Management (SIM): Involves scanning log records for potential threats along with events.
- b) Security Event Management (SEM): Typically examines systems in actual time, informs network managers, and correlates security incidents.
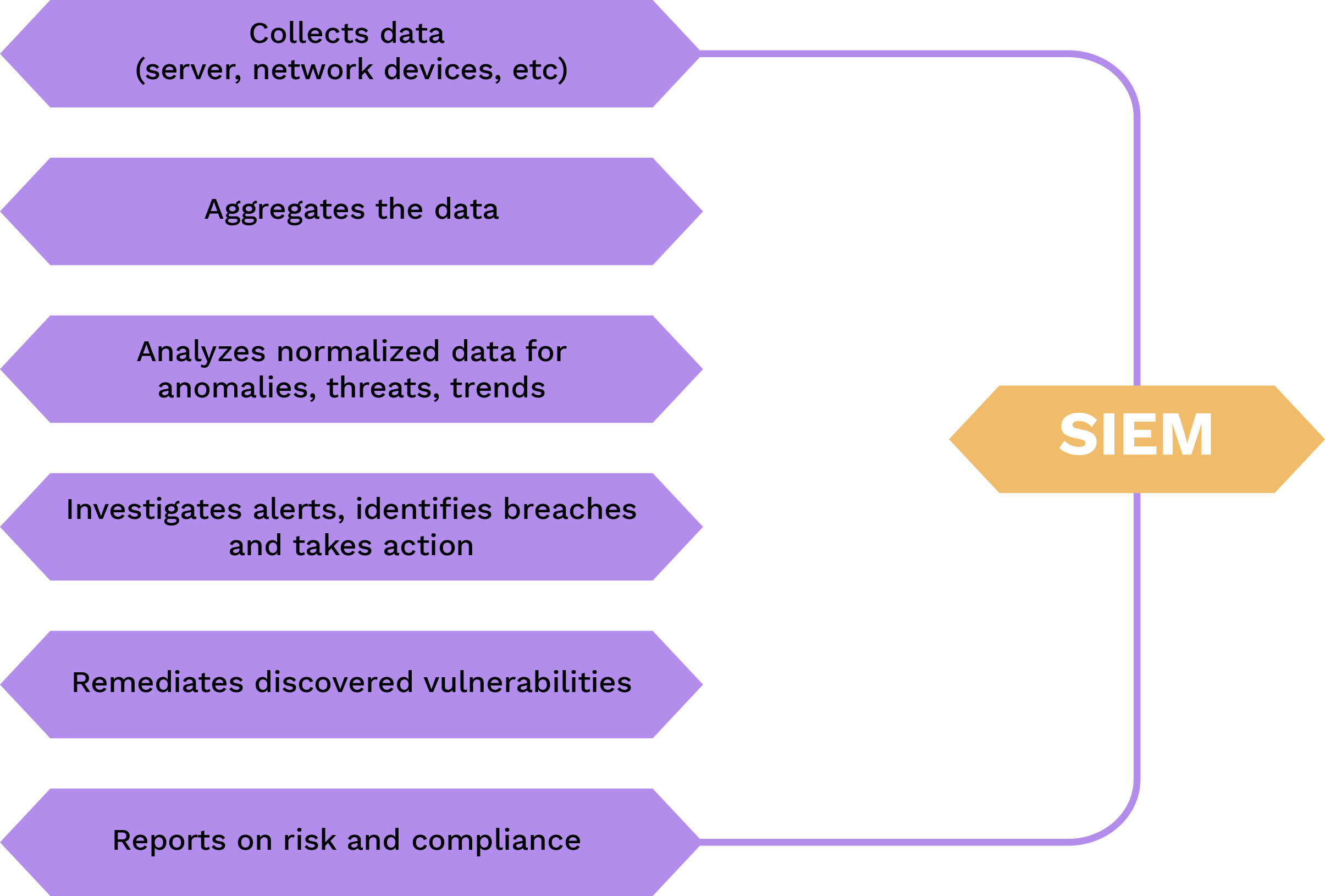
How does it work?
All SIEM systems collect, aggregate, and classify data to detect threats and adhere to data compliance rules. While each system’s‘ abilities vary, the bulk of them provide the same fundamental set of features, which are listed below:
1.Data Collection
SIEM gathers data on events from multiple places across an organization’s IT infrastructure, including both on-site and cloud-based systems. Event log data from users, end points, applications, sources of data, workloads in the cloud, and the networks, as well as data from security software and hardware components such as antivirus software and firewalls, are gathered, correlated, and analyzed in real– time.
Most SIEM systems collect data via installing collecting agents on user devices, servers, network devices, as well as other safety measures such as antivirus and firewall, or by using syslog forwarding, SNMP, or WMI protocols. Improved SIEMs can communicate with cloud-based providers to collect data logs from cloud-deployed infrastructure or SaaS apps, and they can swiftly accept non-standard data sources.
2. Data Storage
SIEMs used to rely on data center storage, which made it difficult to store and handle massive amounts of data.
As a result, just a portion of the log data was preserved. Next-generation SIEMs are built on contemporary data lake technologies like Amazon S3 and Hadoop, which offer infinite storage scalability at a reasonable price. This allows for the retention and analysis of log data from a greater range of platforms and systems.
3.Event Correlation and Analytics.
Event correlation is an essential component of all SIEM systems. Event correlation, which uses powerful analytics to identify and assess specific data trends, provides insight into how businesses may quickly discover and mitigate potential security risks. SIEM solutions significantly improve IT security team’s‘ Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) by offloading manual tasks associated with in-depth security event analysis.
4.Monitoring Iincidents and Sending Security Alerts.
SIEM organizes data into a single, central dashboard from which the security specialists may monitor activities, analyze alerts, detect dangers, and respond or remediate. Most SIEM dashboards also contain real-time data visualizations to assist security analysts in detecting spikes or trends in problematic behavior. Administrators may get timely alerts and take necessary action to remediate vulnerabilities before they become major security issues by using customizable, defined correlation criteria.
5.Compliance Management and Reporting
SIEM tools are popular among businesses that need to fulfil a range of regulatory demands. SIEM is an essential instrument for collecting and evaluating compliance data across the whole organization’s infrastructure because it allows for automated data gathering and evaluation. SIEM tools can offer real-time data on compliance with PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPPA, SOX, and various other standards, minimizing security monitoring tasks and discovering vulnerabilities in time to fix them. Many SIEM solutions have pre-built, out-of-the-box add-ons that may create automatic reports to satisfy compliance needs.
SIEM tools and software
There are many SIEM tools on the market; however, the following are only a few examples.
1.Splunk
Splunk is a huge-data framework that facilitates the collection, management, and analysis of enormous volumes of machine-generated data. The program is used to analyze corporate and web data, manage applications, ensure compliance, and secure information.
2.IBM QRadar
IBM QRadar SIEM is a modular architecture that provides instantaneous insight into the infrastructure of your business, enabling identification of threats and prioritization. You may expand the QRadar to meet your log and flow gathering and assessment needs.
3.LogRhythm
LogRhythm provides a comprehensive range of high-performance security, compliance, and operational capabilities to handle an ever-changing world of threats and issues. It provides diverse, valuable, and actionable information on what is really going on in and around a business IT environment.
4.Exabeam
Exabeam® provides a revolutionary mix of features as a solution that the security teams will want use. Use Exabeam to identify threats, defend against cyberattacks, and defeat attackers.
5.NetWitness
The NetWitness Platform enables security analysts to prioritize, respond, rebuild, survey, analyze, and validate information regarding dangers in their environment, allowing them to respond quickly and correctly.
6.Datadog Cloud SIEM
Datadog Cloud SIEM detects risks to your application and infrastructure in real-time. A targeted attack, a threat intelligence-listed IP connecting with your systems, or an unsecured setup are examples of such hazards. When discovered, a signal is created, and a notice is delivered to your team.
7.Log360
Log360 manages log management, audits changes in your Active Directory (AD) environment, monitors Exchange servers, Exchange Online, Microsoft 365, and publicly accessible cloud settings, provides multiple reports for auditing, and sends out notifications in real– time for crucial occurrences.
8.SolarWinds Security Event Manager
SolarWinds Security Event Manager ensures openness when showing compliance by providing capabilities that allow you to quickly monitor and manage any security incident that takes place throughout your network infrastructure, including the ability to produce thorough and readily customizable reports.
SIEM for IoT device monitoring
IoT Security supports SIEM recording, allowing you to submit data concerning recently discovered devices, security warnings, and weaknesses in devices to your SIEM server for additional processing. Cortex XSOAR enables IoT Security to interact with any sort of SIEM that adheres to the CEF standard.
Once the configuration has been completed, you may begin with an initial export of the whole device catalogue from the IoT security to the SIEM server using XSOAR. Following that, XSOAR requests incremental updates every 15 minutes by default. IoT Security checks the last 15 minutes for newly discovered devices, alarms, or vulnerabilities, as well as changes to any attribute fields of previously detected devices and responds with an update if any are found. In addition to these automatic changes, you can use the IoT Security website to report security alerts and vulnerabilities in devices to SIEM.
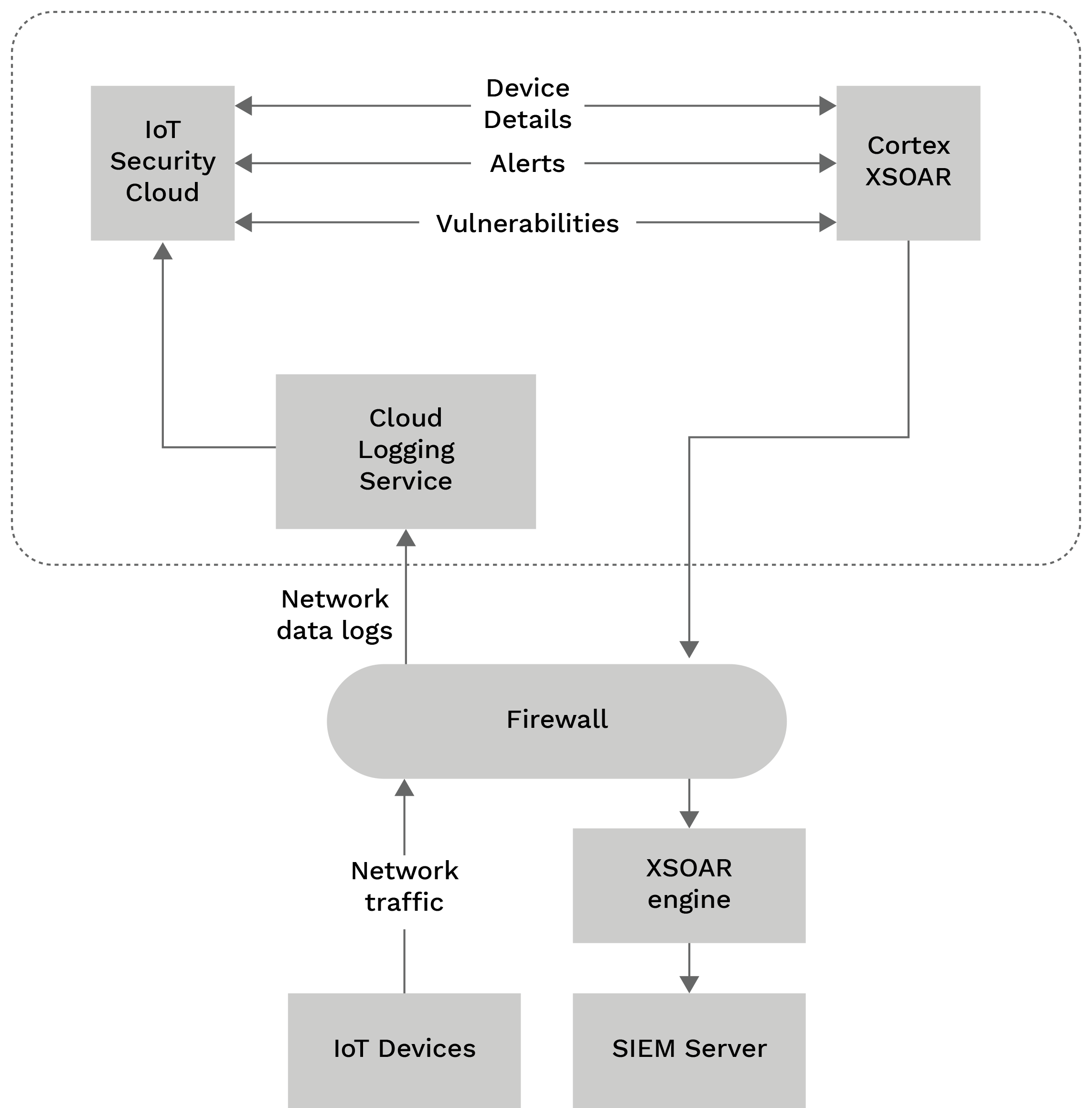
When the configuration is complete, XSOAR makes the initial request to the Internet of Things (IoT) Security throughout the whole device catalogue. After that, XSOAR requests incremental adjustments every 15 minutes. IoT Security determines if any of the device’s characteristic fields have changed since the last time they were updated and, if so, creates a difference. XSOAR and IoT Security employ similar reasoning to identify security vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
Importance
SIEM improves organizational management of security by sifting enormous volumes of security data and prioritizing the program’s security warnings.
Companies can utilize SIEM software to identify vulnerabilities that could otherwise go undiscovered. The program checks log files for evidence of malicious activity. Furthermore, because the device collects data from multiple sources throughout the network’s infrastructure, it can reconstruct the timeline of an assault, allowing a company to analyze the cause of the incident and its consequences on the company’s operations.
The SIEM system may also help a corporation meet compliance requirements by automatically creating reports that include all recorded security incidents from several sources. Without SIEM software, the organization would have to manually gather log data and create reports.
A SIEM system also improves the handling of incidents by assisting the firm’s safety personnel in recognizing the path of an attack across the network, pinpointing the affected sources, and providing automated features to prevent ongoing assaults.
Future Scope
Future advances in SIEM may include the following:
1.Improved orchestration.
Currently, SIEM only automates simple tasks. However, as these organizations expand, SIEM must provide additional functionalities. For example, with AI and machine intelligence, SIEM systems must provide quicker orchestration to ensure all departments within a corporation receive equal security. Moreover, security methods and their implementation will be faster, more effective, and efficient.
2.Improve cooperation with MDR tools.
As the threat of hacking and unapproved access grows, firms must have a two-tier approach for detecting and analyzing security vulnerabilities. A company’s IT staff can utilize SIEM within the organization, or a company that provides managed services may utilize the MDR technology.
3.Improved cloud management and monitoring.
SIEM providers work hard to enhance their products’ cloud administration monitoring and management features in order to better satisfy the security requirements of cloud-based organizations.
4.SIEM and SOAR will be integrated into a single tool.
Traditional SIEM solutions may benefit from SOAR; but SOAR suppliers will most likely respond by increasing their product offerings.
Conclusion
Finally, SIEM solutions play an important role in improving an organization’s security posture. SIEM enables proactive threat detection, efficient incident response, and improved compliance management through advanced analytics and automation. Implementing a SIEM solution should be a top priority for organizations looking to safeguard their valuable assets against today’s sophisticated cyber threats.












