One of the key components of every IoT deployment is IoT gateways. They act as a bridge between the internet and connected devices and are responsible for securing the data that flows between them. Gateways function as the brains of the Internet of Things (IoT), coordinating the data flow between edge devices and central servers. As they have a single point of failure, IoT gateways are frequently targeted by attackers. If an attacker can compromise the gateway, they can gain access to all the data that is being transmitted through it.
To safeguard the whole ecosystem from possible cyber-attacks, it is crucial to secure IoT gateways since they serve as a vital connection that connects local networks to the larger digital infrastructure. In this article, we are going to explore key tactics and recommendations to protect your IoT gateways against potential cyber threats.
What is an IoT Gateway?
IoT gateway is a device that is used to link connected devices to the cloud. It acts as a bridge between the translating data between the different protocols used by the devices and the cloud.
IoT gateways also provide security, data aggregation, and other features that are essential for managing and securing IoT deployments. Here are some of the key functions of an IoT gateway:
Data translation: IoT devices use a variety of protocols to communicate with each other. The IoT gateway translates the data between these protocols so that it can be understood by the cloud.
Security: IoT gateways provide security features such as encryption and authentication to protect the data that is being transmitted between the devices and the cloud.
Data aggregation: IoT gateways can aggregate data from multiple devices and then send it to the cloud in a single stream. This can help to improve the efficiency of data transmission and processing.
Device management: IoT gateways can be used to manage IoT devices, such as updating firmware and configuring settings.
Edge computing: IoT gateways can be used to perform edge computing, which is the processing of data close to the source. This could aid in enhancing the security and performance of IoT applications.
How IoT Gateway works in IoT Devices?
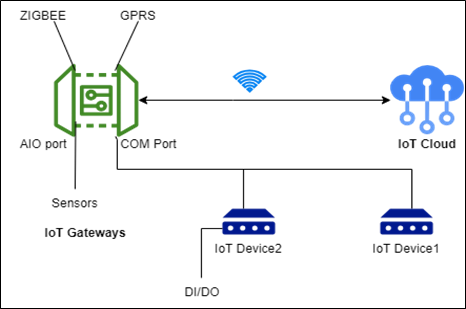
Figure: IoT Gateway Architecture
IoT gateways are placed in between IoT devices and the cloud. They act as a bridge between the two and help in reducing the number of internet connections. They become the target for malicious software which can use the gateway’s flaws to access the IoT network. Many different protocols, including Wi-Fi, Z-Wave, Zigbee, BACnet, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), can be used by IoT gateways to connect to the cloud. The requirements of the application will determine the specific protocol that is employed.
Balancing Connectivity and Security: Strategies
Robust Authentication: Implement strong authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access the gateway and its management interfaces.
Encryption Protocols: Employ robust encryption protocols such as TLS to secure data during transmission between devices, gateways, and the cloud.
Firmware Integrity Checks: Employ secure boot mechanisms to validate and ensure the integrity of firmware loaded onto the gateway.
Network Segmentation: Isolate IoT networks from critical networks through network segmentation, thereby limiting the lateral movement of attackers.
Regular Updates: Regularly update gateway firmware and software to address vulnerabilities and bolster security measures.
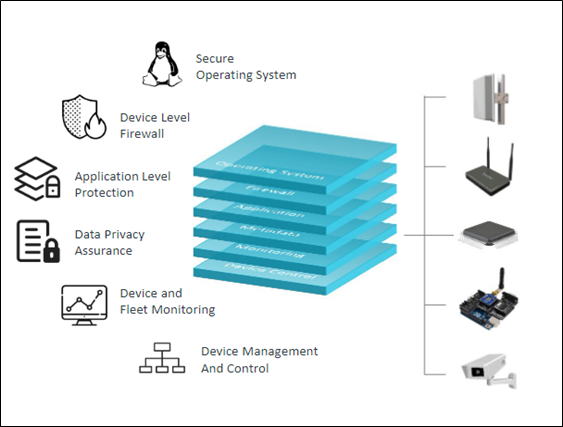
Figure: Multi-Layer Gateway-Level Security
Multi-layer gateway-level security
It is a security approach that uses multiple layers of security to protect gateways. This strategy helps to mitigate the risks of gateway attacks. The different layers of gateway-level security can include:
Authentication and authorization: This layer ensures that only authorized devices and users can access the gateway. Passwords, authorizations, or additional types of authentications are frequently utilized for this.
Packet filtering: This layer examines each packet that is sent to or from the gateway and determines whether it should be allowed to pass. This can be used to block malicious traffic, such as denial-of-service attacks.
Intrusion detection and prevention: This layer monitors the gateway for suspicious activity and takes action to prevent attacks, such as blocking malicious traffic or quarantining infected devices.
Data encryption: This layer encrypts data that is sent to or from the gateway, preventing unauthorized users from reading it.
Logging and monitoring: This layer logs all activity on the gateway, which can be used to troubleshoot problems and detect attacks.
To monitor and safeguard large-scale B2B IoT/IoT networks, cut operating expenses, and create new revenue streams, IoT service and solution providers can use leverage IoT cyber security and analytics software. Multiple levels of security are present in such cyber security solutions, including:
Device-level security: For Linux-based gateways, industrial PCs, and edge devices, the device-level security agent offers continuing, automatic protection.
Vulnerability scanning: The agent scans devices for known vulnerabilities and patches them as needed.
Malware detection: The agent detects and blocks malware from infecting devices.
Data encryption: To prevent unauthorized access, the agent encrypts data while it is in transit and at rest.
Centralized security management: IoT network security can be managed centrally with the help of the Security Manager application.
View device alerts: The application allows users to view alerts from devices, such as those related to security threats or operational issues.
Manage device policies: The application allows users to manage device policies, such as those related to security settings and firmware updates.
Deploy firmware updates: Users can upgrade devices’ firmware using the program.
Wrapping Up
IoT equipment is necessary for any type of organization. For any organization’s IoT assets, businesses must put strong security measures in place if they want to safeguard their assets, data, and infrastructure from potential threats. By putting these procedures in place, organizations can minimize the risk of security assaults.
eInfochips has proven track record in helping organizations manage security products on a global level. At all network layers, including device connection and apps, we are experts in protecting linked device networks. Because of our strategic, transformative, and managed operations philosophies, we can offer full cybersecurity expertise.