The Clipper malware, which first surfaced in 2017 on Windows operating systems, is a relatively unknown threat to most users and companies. It was later discovered on the Google Play store as Android/Clipper and was identified as impersonating a legitimate service called MetaMask.
The main goal of the virus is to take over the victim’s Ethereum funds by stealing their private keys and credentials, but it is also capable of swapping a cloned Ethereum or Bitcoin wallet address with one controlled by the cyber attacker.
Malware that steals information is becoming increasingly prevalent, with Cyber Research Labs having detected the “clipper virus” on a cybercrime forum. However, further analysis revealed that this virus does not function as a Crypto Stealer. Instead, it is a disguised variant of the well-known Clipper virus, which can read and modify any text that the user copies, including crypto wallet information.
What is Clipper Malware?
Clipper is a type of malware that attempts to steal cash from infected systems by altering or stealing data on the Windows clipboard. Microsoft classifies it as cryware, which is malware designed to steal cryptocurrency. Clipper malware steals Bitcoin by modifying the victim’s clipboard activity and substituting the destination wallet with the attacker’s.
The malware is intended to steal Bitcoin by replacing the wallet address in the victim’s clipboard with the attacker’s wallet address. This covert approach aims to deceive the victim into performing a legitimate Bitcoin transaction, with the attacker being the recipient of the stolen funds.
How does Clipper Malware work?
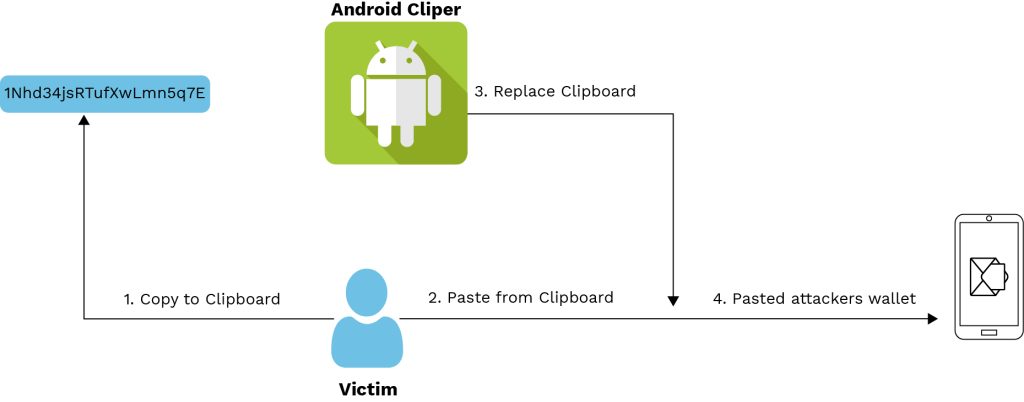
Figure. Process Of Clipper Malware
This class contains the main method that runs the clipper functionality. Upon execution, the main program generates a random mutex designated as ‘1Nhd34jsRTufXwLmn5q7E’ to ensure that only one instance of the malware process runs at any given time. If the mutex fails to construct, the virus ends its operation.
After establishing persistence with the mutex, the virus transfers itself to the starting directory and executes the function ClipboardNotification.NotificationForm(). Clipper malware monitors the clipboard of the infected device that stores copied data. As the user copies data, the clipper examines it to see if it includes any Bitcoin wallet addresses. If it does, the virus replaces the wallet address with the attacker’s address. When the user chooses to paste the address, they end up pasting the hijacked address rather than the legitimate one. The Clipper virus exploits the complexity of wallet addresses, which are long chains of random numbers and letters. It is highly unlikely that a person will notice that their wallet address has been swapped unless they have used it multiple times.
The Rise in Cryptocurrency Attacks
Although this attack vector is not new, it should not come as a surprise. Nowadays, there is a huge market for cryptocurrencies that offers the opportunity to make a lot of money. While most people prefer to earn a living through legal means, some will always prefer to take advantage of others. In the case of Clipper malware, security organizations discovered cryptojackers infiltrating apps on the Google Play store. As a result, this might be only the beginning of cryptocurrency-based malware targeting Android users.
The “clipper” virus, designed for Android devices, operates by surreptitiously swapping the victim’s wallet address with one controlled by cyber attackers, thus enabling them to hijack digital coin transactions. The Android/Clipper.C virus serves a dual purpose, as it can either pilfer users’ passwords and private keys to gain access to their Ethereum holdings, or it can alter Bitcoin and Ethereum wallet addresses that are copied to the clipboard of an infected device. Cybersecurity researcher Lukas Stefanko wrote on Bitcointalk, the popular Bitcoin forum: “Even if you check part of the pasted Bitcoin address, the chances are that the first few characters are the same, and you still won’t notice that the address was changed.”
Clipper Malware Exploits Tor Browser to Steal Cryptocurrencies: Kaspersky Report
In recent times, cybercriminals have increasingly used the Tor Browser as a tool for malware attacks. They distribute a Trojanized version of Tor Browser via third-party resources, which contains a password-protected RAR archive that helps the malware evade detection by security solutions. Once inside the user’s system, the malware disguises itself as a popular application like uTorrent and registers itself in the system’s auto-start, as well as dropping unnoticed.
According to a recent report from Kaspersky, cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and Monero have been targeted in over 15,000 attacks worldwide by clipboard injector malware. Russia is the most affected country due to the official blocking of Tor Browser, leading to users downloading it from third-party sites. The countries that have been most affected by the malware attacks are the United States, Germany, Uzbekistan, Belarus, China, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and France. The actual number of infections may be higher than reported. According to the analysis of existing samples, users have suffered a loss of at least US$400,000. However, the actual loss is likely to be much higher since the research only concentrates on the abuse of Tor Browser, and other campaigns may use diverse software, malware delivery methods, and wallet types.
Clipboard injector malware is particularly insidious as it can remain undetected for years without network activity or other signs of presence. It replaces a crypto wallet address the day it finally decides to strike. “Despite the fundamental simplicity of the fake Tor Browser attack, it poses a greater danger than it seems. It not only creates irreversible money transfers but also remains passive and hard to detect for a regular user,” warns Vitaly Kamluk, Head of APAC Unit, Global Research & Analysis Team at Kaspersky.
How Can You Protect Yourself Against Clipper and Other Android Malware?
Clipper virus relies on the user’s ignorance of its existence and the user’s disregard for warning indicators. To begin to defeat it, always download programs from the Google Play store. While Google Play isn’t perfect, it’s far safer than visiting websites that operate as third-party applications for Android since they are much more likely to contain malware than Google Play. Even if your phone becomes infected with the clipper virus, you may escape an attack by exercising caution.
Check any wallet addresses you paste to be sure they haven’t changed in the middle of the process. To determine if your device has been infected with clipper malware, compare the address you copied to the one you pasted. Additionally, before downloading any app from Google Play, make sure to check its total downloads and avoid downloading newly released apps with a low download count. Verify the developer’s name if the software claims to be the mobile version of a well-known service.
Lastly, ensure that both the operating system and all software are up-to-date and have the latest patches installed. If the malware enters and runs on the system through a known vulnerability, a patched system will almost certainly stop the threat.
To enhance security, consider taking the following 10 measures:
- Never click on links in text messages or emails.
- Be cautious when installing applications.
- Log out after completing online shopping.
- Keep your operating system and applications up to date.
- Turn off connectivity and location services.
- Keep personal information private.
- Do not jailbreak or root your smartphone.
- Have a backup plan.
- Use a mobile security package.
- Physically secure your device.
Conclusion
Clipper is a type of malware that steals information from a victim’s clipboard, allowing cyber attackers to gain access to their target environments. The malware searches for cryptocurrency wallet addresses and replaces them with a similar-looking address controlled by the attacker. As a result, when a user attempts to make a bitcoin payment, it is sent to the attacker’s account instead of the intended recipient.
eInfochips, a global enterprise, has provided assistance in developing, deploying, and managing security solutions by employing strategic, transformational, and managed operations strategies. Their expertise in cybersecurity includes threat modeling and VAPT for devices, OS/firmware, web/mobile applications, data, and cloud workloads while adhering to security industry standards, norms, and recommendations, such as NIST, ENISA, OWASP, MITRE, and IoT Security Foundation, to provide comprehensive security solutions. The company employs a range of machine learning approaches, such as signature-based algorithms, feature extraction, static and dynamic analysis, and various tools, including Virustotal, Process Monitor, Regshot, Wireshark, and Procmon, to detect and classify malware.













