Cybersecurity is the defence against theft, unauthorized access, disclosure, and purposeful or unintentional harm to information systems, including hardware and software. It safeguards all Internet-related components, including networks, the data sent across networks and stored in databases, numerous apps, and devices that use network connections to regulate the functioning of equipment. The Internet has been and will continue to become more pervasive with the advent of new cutting-edge technologies like cloud, mobile computing, fog computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
IoT and IoT Security
The term “Internet of things” (IoT) refers to physical items (or groups of such things) equipped with sensors, computing power, software, and other technologies that communicate with one another and exchange data through the Internet or other communications networks.
IoT security describes the procedures, controls, and tools employed to safeguard IoT systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and online dangers. To secure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of IoT systems and data, it entails putting security mechanisms including authentication, encryption, access control, network security, data storage security, privacy protection, monitoring, and physical security in place.
Big Data and Big Data Analytics
Big data is the term for exceptionally massive and complicated data sets that can be processed more quickly than using conventional data management and analysis technologies. Simply saying, big data refers to larger, more intricate data sets, particularly from fresh data sources. The sheer size of these data sets makes it impossible for conventional data processing technologies to handle them. However, you may use this enormous amount of data to address business issues that were previously impossible to handle.
Big data analytics is the study and discovery of significant patterns, insights, and trends within huge and complicated sets of data. Massive amounts of data from numerous sources, including social media, sensors, and transaction records, must be analyzed using cutting-edge techniques and technologies. The objective is to gather insightful data that will aid organizations in making wise decisions, enhancing performance, spotting opportunities, and resolving issues. Big data analytics is the process of uncovering priceless knowledge buried within immense amounts of data to acquire priceless insights. Big data analytics is the use of advanced analytic techniques against very large, diverse big data sets that include structured, semi-structured and unstructured data, from different sources, and in different sizes from terabytes to zettabytes.
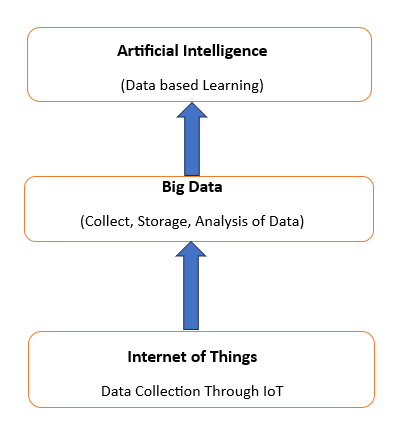
The Internet of Things (IoT) holds great promise for a variety of IoT applications, including healthcare, smart manufacturing, industrial 4.0, and smart homes, which generate great volumes of data that must be processed and shared and may contain sensitive information that must be protected before sharing with others. The data generated by IoT devices is also known as big data, which comprises both structured and unstructured data. It is challenging to handle and analyze large data to uncover significant information that can aid in decision-making because of the complexity of the data. On the other side, a crucial necessity for IoT big data systems is data security.
Big data security is the term used to describe the safeguarding of significant amount of data that is gathered, processed, stored, and analyzed by big data systems. Making sure that data is secure becomes more crucial as it continues to expand rapidly in volume. Data privacy, confidentiality, integrity, and availability are a few of the many facets of big data security.
- Data encryption: Sensitive data can be encrypted while it is in transit and at rest to help prevent unauthorized access. Data may be secured using encryption methods like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
- Access control and authentication: Strong authentication and access restrictions are used to make sure that only authorized individuals may access and modify the data. Role-based access restrictions, multi-factor authentication, and secure authentication methods are all examples of this.
- Data anonymization: Anonymization techniques can be used to remove or obscure identifying information from sensitive data or Personally Identifiable Information (PII) while still enabling analysis of the data.
- Storing data securely: Data may be protected from unauthorized access or alteration by using secure storage solutions like encrypted databases, distributed file systems, or cloud storage with strict access restrictions.
- Network security: Implementing firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and secure network protocols (SSL/TLS) helps safeguard data during transmission and protect against network-based attacks.
- Data monitoring and auditing: Monitoring data access, updates, and user actions on a regular basis makes it easier to spot any shady or unauthorized activity. For tracking and looking into security occurrences, audit logs should be kept.
- Data policy and governance: Clear data governance rules, including instructions for data classification, retention, and destruction, assist to assure data security and conformity with pertinent laws.
- Threat detection and response: Real-time monitoring and machine learning-based anomaly detection are two examples of sophisticated security technologies that may be used to detect risks early and respond to security issues quickly.
- Third-party and vendor risk management: It’s critical to evaluate their security procedures and make sure they abide by proper security requirements while working with external service providers or exchanging data with partners.
- Employee education and information: The danger of insider threats and human error may be considerably decreased by educating employees about data security best practices, such as robust password management, phishing awareness, and social engineering prevention.
Big data generated by the Internet of Things (IoT) can be used to detect cyber-attacks by analyzing the enormous volume of data to look for trends, abnormalities, and warning signs of future assaults. Here are some techniques and approaches used for cyber-attack detection using big data in the context of IoT:
Logic Analysis: IoT devices provide log data that records their interactions, activities, and occurrences. Finding unusual or suspicious patterns that can point to a cyber-attack can be done with the use of this log analysis. Organizations can identify potential attack activities by utilizing log analysis techniques including log correlation, anomaly detection, and pattern recognition.
Anomaly detection and machine learning: How to use the regular behavior patterns of IoT devices and networks can be learned through machine learning algorithms trained on historical data. Machine learning algorithms can look for variations from the norm that can be signs of a cyberattack by analyzing the real-time data produced by IoT devices. Unusual network traffic, unauthorized access attempts, or unexpected device behavior can all be found using anomaly detection techniques.
Threat Intelligence Integration: Organizations can correlate IoT data with well-known indicators of compromise and attack signatures by integrating threat intelligence feeds and databases with big data analysis. Organizations can spot potential attacks and take precautions by comparing IoT data with threat intelligence data.
Behavioral analysis: Cyberattacks can be discovered by examining user and IoT device behavior. Any deviations or odd actions can be identified as potential assaults by establishing baselines of normal behavior. Unauthorized access, data espionage, and other hostile activity can be detected using behavioral analysis approaches, such as User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA).
Network Traffic Analysis: IoT device-generated network traffic data analysis can reveal information about prospective cyberattacks. Organizations can see signs of attacks, such as DDoS attacks, botnets, or network invasions, by observing network traffic patterns, unusual communication flows, or excessive data transfers.
Real-time Response and Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of IoT data streams made possible by big data analysis enables quick identification and reaction to cyberattacks. Organizations can use technologies like stream processing and complex event processing to analyze data in motion and launch automated or alert responses to ominous activity.
Data fusion and Correlation: A comprehensive understanding of the IoT ecosystem can be obtained by fusing data from various IoT devices, sensors, and systems. Finding trends or abnormalities that can point to a cyber-attack can be accomplished by comparing data from numerous sources. The correlation of data streams can improve attack detection precision and minimize false positives.
Advanced Analytics and Visualization: Cyber-attack detection can be aided by using advanced analytics techniques like data mining, pattern recognition, and visualization. Security experts can obtain deeper insights into the IoT data by using complex algorithms and visualising the results. This makes it easier to spot attack patterns or dubious activity.
IoT Security: Big Data Challenges and Opportunities
Opportunities
- Threat Detection and Prevention: The ability to identify patterns, anomalies, and trends in IoT data is made possible by big data analytics that improves threat detection and prevention capabilities. Large-scale data analysis can reveal hidden trends and shed light on possible security vulnerabilities.
- Predictive Analytics: Big data methodologies may be used to foresee security risks and weaknesses in IoT systems. Potential security vulnerabilities may be recognized proactively by analyzing previous data and utilizing machine learning algorithms, enabling the implementation of preventive measures.
- Contextual Intelligence: By combining information from many sources, big data analytics may provide contextual intelligence. This enhances security decision-making by enabling a thorough understanding of IoT ecosystems, including device behavior, network interactions, and user habits.
- Security Analytics and Incident Response: Big data analytics can help in the reaction to security incidents by giving real-time information about ongoing security occurrences. Prioritizing and handling security events more successfully can be achieved with the aid of data analysis from various devices and sources.
- Improved Access Control and Authorization: In IoT systems, access control and authorization processes can be improved with the help of big data tools. Anomalies can be found by examining user behavior and access patterns, which enables more precise and fine-grained access control settings.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: IoT security compliance and regulatory standards can be met with the use of big data analytics. Organizations can guarantee compliance with privacy laws, data protection legislation, and sector-specific security standards by analyzing and monitoring data.
Challenges
- Data Volume and Velocity: The enormous volume and speed of data produced by IoT devices provide serious security challenges. Real-time data management and processing can be challenging and resource intensive.
- Data Complexity and Variety: IoT devices produce a wide range of data kinds, including both structured and unstructured data from several sources. It might be difficult to integrate and analyze such a wide variety of data formats, necessitating advanced data management and analytics tools.
- Data Security and Privacy: Data security and privacy issues are brought up by the collection and transmission of sensitive data by IoT devices. Important problems include establishing encryption, access control, and secure communication connections at all stages of data protection.
- Real-time analytics and response: To ensure IoT security, threats must be promptly identified and countered. There are technical issues that need to be resolved when performing real-time analysis on massive data streams and putting automated reaction mechanisms in place.
- Scalability and Resource Constraints: Scalability is a major problem in IoT ecosystems because there can be a lot of linked devices. Effective resource management is necessary to handle the enormous volume of data produced by IoT devices while considering resource limitations such as processor speed, memory, and bandwidth.
Conclusion
For any organization, IoT device security must be guaranteed. It is crucial for businesses to have strong security measures for their IoT Solution and Services in place to safeguard assets, data, and infrastructure from possible attacks. Organizations may lessen the likelihood of successful attacks and the effect of an event by putting these safeguards in place.
eInfochips has been essential in helping businesses manage security goods on a worldwide level. Our area of expertise is the security of connected device networks at all layers, including device connection and applications. We can offer thorough cybersecurity knowledge because of our strategic, transformative, and managed operations methods. To do this, it is necessary to model threats and perform Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) on OT/IoT devices, operating systems/firmware, web/mobile apps, data, and cloud workloads. Our procedures comply with industry norms, rules, and recommendations like those set out by NIST, ENISA, OWASP, MITRE, and the IoT Security Foundation.













