Abstract:
In recent years, the automotive industry has undergone a significant transformation, leading to the technological advancement of road vehicles both in terms of connection and digitally. This exposes vehicles to more cyber-attacks. Due to the advancement of road vehicles and robust cybersecurity measures, in the automotive industry, uniform rules and standards have become pivotal. A key standard for automotive cybersecurity established jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) is ISO/SAE 21434, particularly for establishing Cyber Security Management Systems (CSMS).
In combining with the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), Regulation No. 155 (UN R155), which strongly mandates CSMS for new vehicle types, to achieve UN R155 compliance, ISO/SAE 21434 compliance is recommended, as it outlines a framework for managing cybersecurity risks during the product lifecycle. The major contributions to this article are mentioned below:
- Enlighten the team on the standard ISO/SAE 21434 framework
- Compliance with ISO/SAE 21434 and UN R155 and its importance
- Core areas of ISO/SAE 21434 for CSMS
- The eInfochips journey towards ISO/SAE 21434
1. Introduction
The automotive cybersecurity standard, ISO/SAE 21434 [1], has been developed to establish CSMS for on-road vehicles. This standard recommends that OEM and suppliers manage cybersecurity culture, policies, and risks in every phase of the engineering process through some guidelines. The standard suggests ways to manage cybersecurity risk throughout the product’s life cycle. The specific technical solutions have not been prescribed in the standard. However, to manage cybersecurity risks for several types of road vehicles, a generic framework has been established.
2. ISO/SAE 21434 Framework
2.1 Purpose
ISO/SAE 21434 was established to provide a framework for cybersecurity risks management in road vehicles, covering the entire product lifecycle.
2.2 Scope
It covers the electronics & electrical (E/E) systems, including software, associated components, and interfaces, in mass-produced road vehicles.
2.3 Requirements & Solutions
In ISO/SAE 21434 standard, the detailed engineering requirements for establishing and maintaining a CSMS in road vehicle E/E systems, from concept requirements to decommissioning, are systematically outlined. In product development lifecycle, the integration of CSMS is the key challenge for the manufacturer. The CSMS was added as an augmentation to the existing tools in the starting phase of the standard implementation. Moreover, there is rigorous work going on to develop solutions to integrate into the development process more flawlessly. ISO/SAE 21434 is seen as a standard that provides guidance on how to meet the requirements of UN R155 [3].
2.4 Framework
Figure 1 represents the detailed ISO/SAE 21434 framework to maintain throughout the product lifecycle of road vehicles. The standards are classified into different clauses. Clauses 4 to 7 focus on general organization, project specific management requirements and the coordination of cybersecurity activities. Clauses 8 to clause 15 deal with the concept and development to decommissioning.
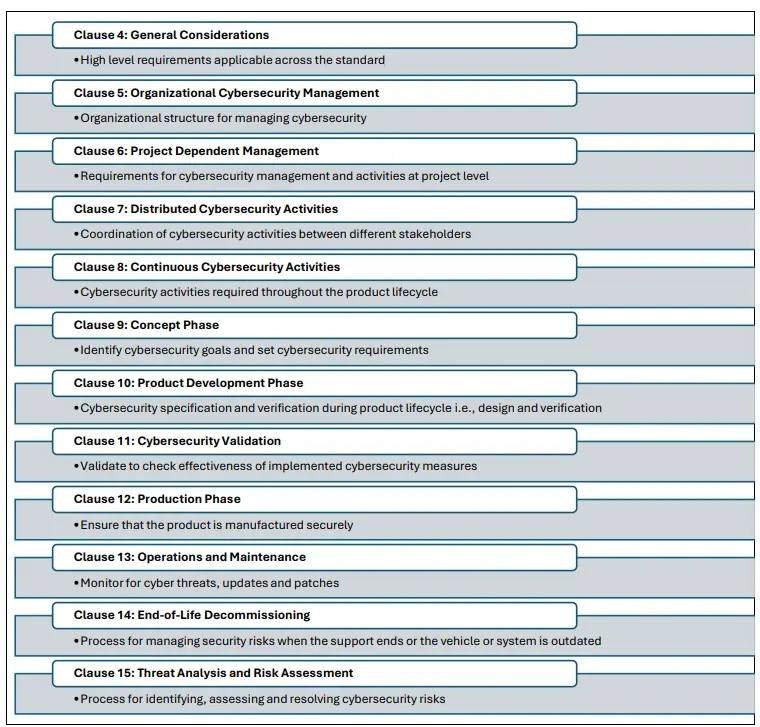
Figure 1: ISO/SAE 21434 Framework
3. Compliance with ISO/SAE 21434 & UN R155
This section outlines the guidelines, basic requirements, and importance of compliance with ISO/SAE 21434 & UN R155.
3.1 Compliance with ISO/SAE 21434
3.1.1 Requirements
Compliance with ISO/SAE 21434 is not mandatory; it is recommended. Non-mandatory standards can be adopted by automotive industries worldwide.
3.1.2 ISO/SAE 21434 Compliance Guidelines: Complete Process Overview
The process involves all stages of concept and development to maintenance, ensuring that cybersecurity is integrated throughout the lifecycle. To achieve compliance with ISO/SAE 21434, a few guidelines are mentioned in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Guidelines for Cybersecurity Compliance with ISO/SAE 21434
Figure 2 ensures that cybersecurity is integrated into each stage of the development process, maintaining compliance with ISO/SAE 21434 and ensuring the safety and security of automotive systems throughout the product lifecycle.
3.2 Compliance with UN R155
3.2.1 Requirements
UN R155 mandates that all new vehicle types undergo cybersecurity approval, and it requires manufacturers to establish a CSMS.
3.2.2 CSMS Requirements
The standard defines requirements for the establishment and maintenance of CSMS, covering organizational structure, risk management practices, and cybersecurity engineering processes.
3.2.3 ISO/SAE 21434 as a Solution
ISO/SAE 21434 is considered a standard that offers guidance on fulfilling the requirements of UN R155.
The need for compliance: Non-compliance with ISO 21434 and UN R155 can result in sales bans in UNECE member countries, financial penalties, and significant reputational harm.
4. Core Areas of ISO/SAE 21434 for CSMS
4.1 Risk Management
The essential part of the standard is the implementation of a detailed TARA to detect and assess significant risks and vulnerabilities.
4.2 Cybersecurity Engineering
It provides guidance on integrating cybersecurity measures throughout the development lifecycle—from design and implementation to verification and validation.
4.3 Continuous Improvement
The standard offers continuous monitoring, event assessment, and incident response to ensure security throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
5. eInfochips journey towards ISO/SAE 21434
- ISO/SAE 21434 work products templates are prepared for compliance documentation.
- In compliance with ISO/SAE 21434, TARA at the High Voltage DC-DC Converter (HVDCDC) ECU level has been defined and implemented.
- To ensure HVDCDC to be compliant with ISO/SAE 21434, the relevant cybersecurity work products are thoroughly documented, verified through the process and baselined in accordance with the standard.
- The team developed and implemented various required security controls as per the standard guidelines.
- Static and dynamic code analysis has been performed in compliance with MISRA C and CERT C standards.
- Verified & validated cybersecurity work products to ensure the HVDCDC secure operation.
6. Conclusion
Through this blog, the audience will understand the complete ISO/SAE 21434 framework, the process, guidelines for achieving the ISO/SAE 21434 compliance, and the requirement of security standards for the compliance of UN R155. Moreover, the case study showcases the capability and accomplishments of eInfochips on the HVDCDC compliance with ISO/SAE 21434.
Know More: Automotive Cybersecurity











