This is the second blog in the series of ‘Digital transformation in EV charging value chain’ and focuses on the importance of OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) for the EVSE manufacturers and Charging network service providers.
Did you know that General Electric (GE) was the first company to introduce EV chargers in the early 1900s? Although the initial developments in EVs were breakthroughs but failed to go mainstream due to the lack of a standardized approach (i.e., connectors, protocols, etc.). With growing EV sales and mass-market opportunities, the industry stakeholders have started adopting common standards and protocols.
EV charging protocols such as OCPP are helping to overcome the bottlenecks of proprietary protocols such as vendor lock-in and foster open interoperability between hardware and software solution providers. In this blog, we will see what OCPP is, an overview of its versions, and key considerations of OCPP implementation.
OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol)
It is an open-source communication protocol regulated by Open Charge Alliance. It has become a de-facto standard enabling transparent communication between EV chargers and the backend charging station management system (CSMS).
It is a license-free and vendor-agnostic protocol to exchange vital charging information such as start/stop of charging sessions, charger management, firmware upgrades, and many others between chargers and the back-end system. The following diagram shows where OCPP sits in the EV charging ecosystem.
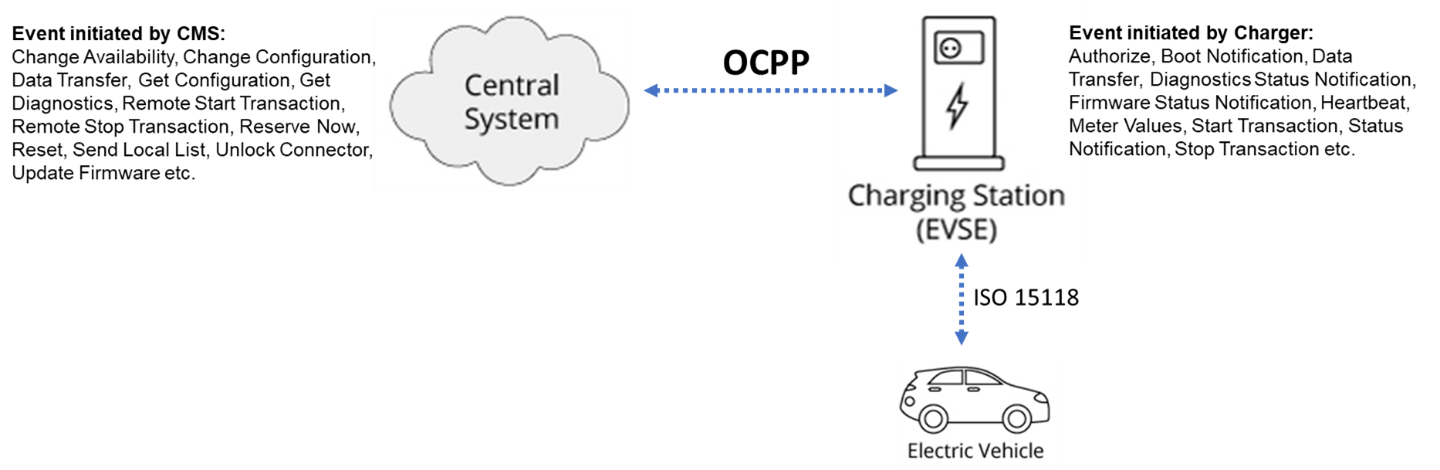
Before OCPP, switching to a different charging software (offering better pricing and incentives) or selecting new charger equipment (offering new technology and features) was difficult due to closed systems working on proprietary communication protocols.
In a simple analogy, it is like buying a mobile handset working with a single operator for a lifetime. Before we move further, let’s understand the types of charging station networks:
| Non-networked | Closed networks | Open networks |
| Charging stations work as stand-alone units with no network connectivity. | EV chargers based on proprietary protocols to communicate with charging networks. | Allows owners of charging stations to flexibly switch between charging networks and equipment vendors without any change in infrastructure. |
| Uses the standard electricity rates offered by the grid supplier. | Typically needs entire system replacement to switch to other networks or charging equipment due to vendor lock-in. | Offers enhanced security and integration with energy management systems and V2G applications |
| Example: Residential chargers | Example: Tesla chargers | Example: OCPP compliant EV charger and software |
Benefits of OCPP
- Flexibility – OCPP enables operators to choose from chargers offering the latest technology and software offering better pricing & features.
- Interoperability – OCPP is vendor-agnostic, meaning any OCPP compliant hardware or software can work with each other without any change in the infrastructure.
- Scalability – Operators can add new chargers from different vendors or select new service providers as required.
- Future-proof – OCPP is vendor-agnostic, which means the investment made in OCPP compliant EV charging stations is safe.
OCPP Protocols at-a-glance
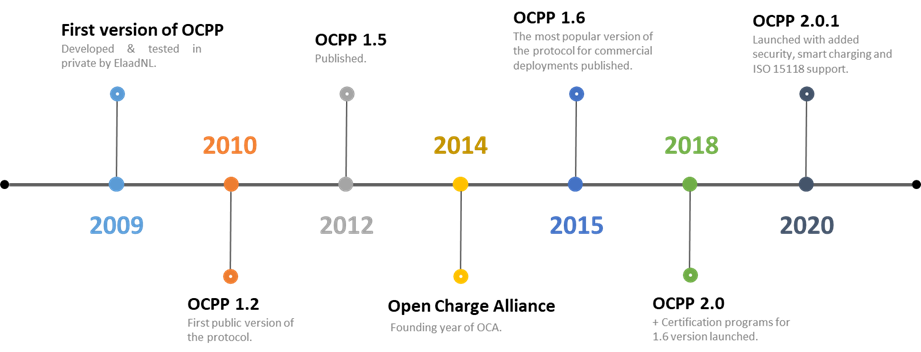
OCPP 1.2/1.5: Based on SOAP, served as the foundation for today’s matured OCPP protocols before OCA was founded.
OCPP 1.6: It is a widely used protocol for commercial applications due to its early availability. It supports both SOAP and JSON-over-WebSocket. The protocol has been updated over time including support for smart charging features, security, and a certification program to validate the protocol implementation.
OCPP 2.0.1: It is the latest OCPP protocol, launched in 2020 with added functionalities of device management, smart charging, ISO 15118 (V2G) support and enhanced security measures, etc. Unlike OCPP 1.6, there is no need for a dedicated VPN between the charge point and back-end system to ensure security.
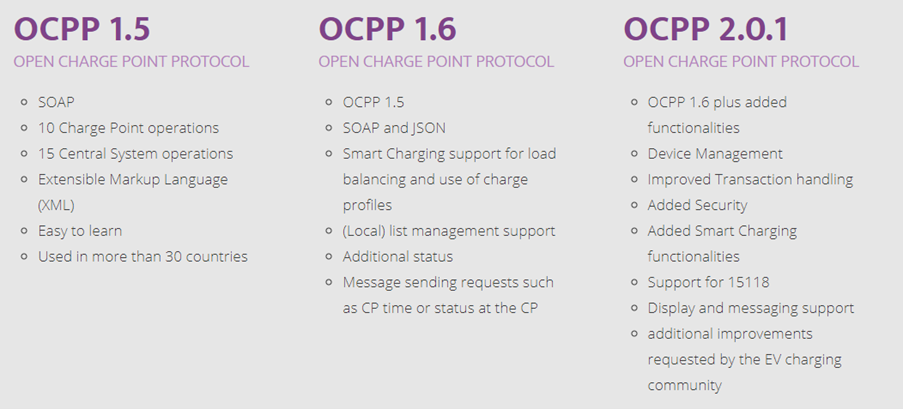
Key considerations while implementing OCPP protocol
Protocol selection: The earlier version of the OCPP (i.e., OCPP 1.5) was based on SOAP that uses XML to represent data which is very bulky and not ideal for charge points with moderate internet connectivity. In contrast to SOAP, OCPP 1.6 & 2.0.1 protocols support JSON-over-WebSocket which is modern technology and simplifies communications using OCPP client-server architecture.
In contrast to OCPP 1.6 supporting limited authorization mechanisms, OCPP 2.0.1 supports multiple options such as remote transactions, Plug & Charge and PIN, etc. OCPP 2.0.1 is also a clear choice for implementations requiring support for ISO 15118 and integration with energy management systems (EMS).
Integration testing: Once the basic implementation of OCPP is done, it is important to test various communication scenarios and interoperability between the charger (client) and back-end (server). This includes operations initiated by the charger (i.e., Authorize, boot, heartbeat, start/stop, metering, status, etc.) and EV users via mobile app (i.e., remote start/stop, availability check, reserve, etc.)
OCPP migration: Although the latest OCPP 2.0.1 offers improved features (i.e., device management, security, smart charging, etc.), one should carefully consider migration due to inconsistent protocol interpretation. There are two ways of performing migration – instantaneous and iterative. For a successful migration, consider checking if back-end infrastructure supports 2.0.1, change in the naming conventions, cost of migration, and proof of concept before full migration.
The way forward
OCPP compliance for EV charging hardware & software has become inevitable due to the growing requirements of interoperability. It has a great potential to be adopted as an ISO (standard) in the future and EV charging vendors should seek expert assistance for OCPP implementation & testing and developing a future-ready product roadmap.
eInfochips is at the forefront of next-generation EVSE/EV charging station design and development. It has successfully executed award-winning projects in compliance with the OCPP and has in-depth experience in working with both OCPP 1.6 and OCPP 2.0.1 protocols.
eInfochips offers turnkey design and development services including hardware/firmware development, charging protocols, wireless connectivity, smart HMI, IoT & Cloud integration, cybersecurity, blockchain, smart charging Apps, V2G applications, and system-wide QA/Test automation framework. To know more, contact our experts today.













